Generally speaking, mobile network operators (MNOs) were highly disruptive in the 90’s, but have continued to decrease in this over the last decade. Operators are no longer the offensive, attacking force of yesteryear, instead they’re putting up barriers and defensive walls trying to protect what they have and hide.
Instead, the disruption comes from the open web. Whenever the operators put up a blocker to what users want, usually in the form of price or access to their infrastructure, the web finds a way of displacing them. Examples abound in location based services, text messaging, video and photos.
There’s a reason operator revenue is shifting away from voice and SMS towards data. The products that got the operators here are receding in relative value. The user wants what’s available in the open web, and that’s just not found, or being provided, by the operators.
So, what is an MNO to do?
Change. Disrupt someone else. Innovate.
One of the biggest disruptors, even in this decade of MNO mediocrity, has been Safaricom – the 800lbs gorilla in my own back yard. They’ve invested in new technology, products and business models like few others, and are reaping the rewards of those strategic moves.
Do I like having a monopoly player in my market? No.
Do I feel bad for the other MNOs (Orange, Airtel and Yu) who are crying now? No, they did this to themselves.
Let’s dig into their golden-child, Mpesa, the mobile peer-to-peer payment system that’s did $3.15 billion in transaction in just the last 6 months(!). How do you know they succeeded in innovating? Well, the easy answer is looking at their profitability and user tie-in that they get from Mpesa. Look more closely and you’ll notice the other signal, all of the bank lobbies in other countries have put up huge walls, blockading an aberration like Mpesa from having sway in their country.
[Sidebar: A warning to everyone who wants to see innovation in their country. Over regulation of telecommunications and banking strangles it. South Africa and Nigeria are cases in point.]
So, Mpesa sounds to everyone like a huge success story. It is, and it’s not. What we think of as an amazing disruptive product is really only halfway up the mountain. There are too many corks being popped while money lies sitting on the table. This stems from 2 main things, which seem to be an issue of Vodafone primarily, since they own the IP for Mpesa and own a 40% stake in Safaricom:
- The lack of leadership by Vodafone to NOT open up an API that other businesses could build on and increase usage. They’ve stifled innovation on their own product.
- Their lack of vision in the global payments space. Their shortsideness in not spinning out Mpesa as its own company to take on Visa and Mastercard directly. This was one of the few products and business models that could do that.
More MNO Innovation
So, Safaricom might be stifling its own product, but they’re still not short on disruptive features and products. They do fall prey to bureaucracy and political infighting, but they’re also one of the most aggressive MNOs globally, always trying new things. Three more examples:
- Creativity in 3g data pricing and accessibility down market.
- First-movers in 3g and exceptional data coverage countrywide.
- Okoa Jihazi, their product that gives a loan of credit from the operator to users who are tight on cash.
Other examples of MNOs who are innovating in Africa are:
Airtel Madagascar working with Movirtu with their new Cloud Phone, a way for people to share a phone, but keep the SIM card in the cloud.
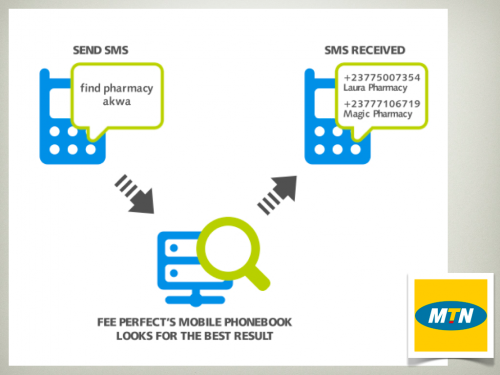
MTN, testing Mobile Phonebook by FeePerfect out of Cameroon, a product that puts a phone book into everyone’s phone.
Small + Big
Clearly, innovative products can come to market through MNOs. What’s the common denominator on these products though? Most of them came from small companies and were then incorporated into the MNO.
Ideas come from outside, they come from the edge. Scale comes from inside, from the massive infrastructure provided by the MNO. They have to work together to succeed.
I work with, and talk to, hundreds of entrepreneurs. They have ideas, prototypes and products that just might be what the users want. They lack the access to the infrastructure to roll it out.
As an MNO, you boost your chances of success in this increasingly chaotic space by not walling everything off, but by opening it up.