[warning: not your normal tech-in-Africa post, continue at your peril.]
I’ve been off on a mini-family vacation, unconnected from the grid – not even taking my mobile phone with me. It gave me time to think, and one thing I started thinking about was the world I grew up in, and how my daughters are growing up today. It brought to mind a recent post by Ethan Zuckerman, and how it hit home to me. It’s who I am, and might help explain why I do what I do.
What are bridge figures, xenophiles?
(Stolen shamelessly from Ethan Zuckerman, please go read the rest):
Xenophiles are people who are fascinated by the whole world, by things other than their ordinary experience. They’re people who want to connect with people who see the world very differently. Some of these people are born this way, lots more are made – a good recipe for xenophilia is to raise a child in a culture deeply different from that of her parents – people call these kids “third culture kidsâ€. Third culture kids have one foot in each of two cultures – the culture of the country they grew up and the culture of their parents, and as a result they don’t really live in either, but a little bit in both. Some kids hate this – many love it, and they end up bridge figures, natural xenophiles who can help translate cultures for other people. Barack Obama’s one of them.
It’s my theory that xenophiles are going to be very powerful in the future. We’re living in a world that the pro-globalization folks refer to as “flatâ€. That’s bullshit, obviously. The world is flat as far as stuff is concerned. In my hometown of 3000 people, I can get water from Fiji and fish from Chile, but I’m not going to encounter any Fijians or Chileans. I’m not even likely to encounter information from those countries, news, opinion or cultural influences like films or TV… not unless I very actively go looking for it. So the world’s flat in terms of stuff, but not in terms of human interaction. It’s flat, but in the least important ways – in the ways that matter, in the ways that would allow us to connect with people from other cultures, allow us to share ideas and solve problems together, the world is disconnected. It’s lumpy.
Xenophiles are good at making connections in this lumpy world. It’s a good idea to have them if you’re trying to do business in another country – some of the people who are making lots of money in this economy are people from developing nations who study in Europe or America and then return home. They can bridge between cultures in a way that helps them make smart economic decisions. They’re even more important if you’re concerned with security or with diplomacy, because their ability to cross cultures makes it far more likely that they can collaborate and create solutions with people from other cultures.
Normal is relative
I don’t think it strange at all switching from the US to Africa and back again. You shift, that’s all.
When you grow up like we did, “normal” to you isn’t the same as “normal” to either the Africans you live with or the US family you go see every 4 years.
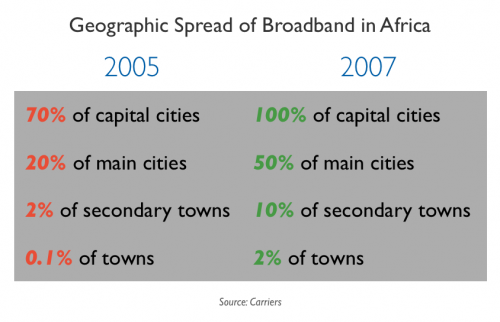
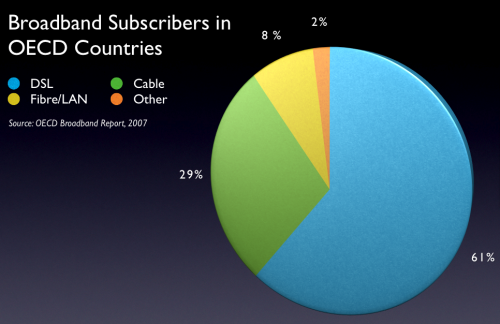
It’s what makes these images look so strange to some people, yet so normal to me.

My daughter taking a bath in Uganda. The lady closest to her, Alice, I called mama mbili – my second mother growing up. She’s part of why I find it easy to switch gears so easily.

This one is me back in 1978 or so, way out in the bush in Southern Sudan where my parents worked with the Taposa tribe doing Bible translation.
There really isn’t that many of us yet relative the all the “normal” people, but the bridgers, xenophiles and third-culture kids of the world tend to either have an inordinate impact or be spectacular failures. Maybe average is just a little harder for us to achieve?

 Next time I’m in Orlando, I’m going to see Scott Johnson. He lives about an hour away in Daytona Beach and has developed a solar-powered Internet “hub” system (running Ubuntu GNU/Linux) that he builds to order. In the video below, he talks about the what, why and how of his system. Incredible work, and well worth watching.
Next time I’m in Orlando, I’m going to see Scott Johnson. He lives about an hour away in Daytona Beach and has developed a solar-powered Internet “hub” system (running Ubuntu GNU/Linux) that he builds to order. In the video below, he talks about the what, why and how of his system. Incredible work, and well worth watching.