When we pushed the first version of Ushahidi live in Kenya, I was trying to juggle that as I spoke at a conference in New York. Today, we’re deploying the new Ushahidi Engine (v0.1) into the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and I’m in Rhode Island speaking at another conference. I’m starting to see a pattern emerge…
Reporting Incidents from the Congo
The DRC deployment can be found at http://DRC.ushahidi.com, and the mobile number to send SMS reports to is +243992592111.
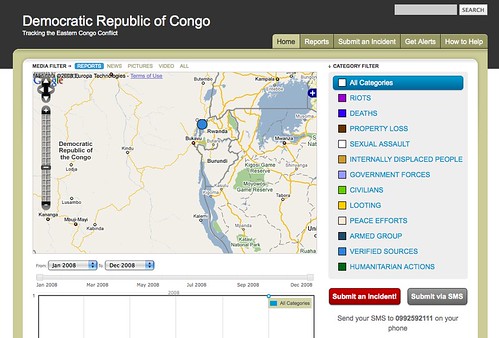
Note: This is the alpha software for Ushahidi. If you find any problems, please submit them to bugs.ushahidi.com.
How you can help
Get the word out. Let people know the mobile number (+243992592111) and website (drc.ushahidi.com). Help get word to the Congolese on the ground in the DRC of this tool, that’s who needs to know about it.
Things are serious in the Congo… They are bad, very bad. As Sean Jacobs states:
“Since August this year at least 250,000 people have been left homeless in Eastern Congo in the latest outbreak of a civil war described here as between government troups and a rebel group claiming to protect ethnic Tutsis. At least 2 million people are refugees from that war which dates back to 1996.”
It’s a difficult situation, with a swirling mixture of militia and armed forces, compounded by particularly brutal and confusing activities. External military forces, years of displacement and a misinformation mar the landscape.
A new Ushahidi, a new test
To be quite honest, we’re a little nervous, just as we were the first time. The new engine still has a few bugs, and there are some process flow issues that we’re still trying to get figured out. This time we’re backed up by a group of competent developers who are working to get things straightened out. Want to help us make it better? It’s an open community, and we’re looking for your input.
We are VERY interested in hearing from you on how we can make the system better. If you have ideas, thoughts, comments – tell us. Leave them in the comments here, on the Ushahidi blog, or on the Ushahidi contact form.
This is a test of the system, albeit a very difficult one, but it will affect the way the software is changed, modified and upgraded in the next version. What we get right here, we can make work for you in your area when you need it.
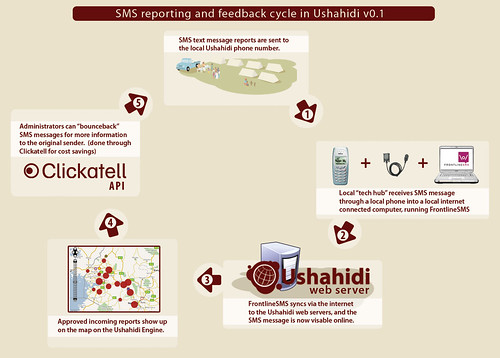
How SMS messages route through Ushahidi
This simplified graphic was created to show how SMS messaging moves through the Ushahidi system – it’s a 2-way communication cycle.
- An SMS gets sent to a local number
- It passes through FrontlineSMS
- This syncs with Ushahidi
- The message shows up on Ushahidi
- Admins can decide to send a message back to the original sender
We use FrontlineSMS so that we can provide local numbers in areas where the larger SMS gateways don’t operate. For instance, if you were to try to run this in Zambia, you’d probably get a UK phone number if you went through Clickatell. However, we do use Clickatell for the messages that we route back to the original sender due to cost savings. They also have a very nice, easy to use API.




 UNICEF has two interesting skunkworks-like projects (among many more) that they talked about today.
UNICEF has two interesting skunkworks-like projects (among many more) that they talked about today. 
