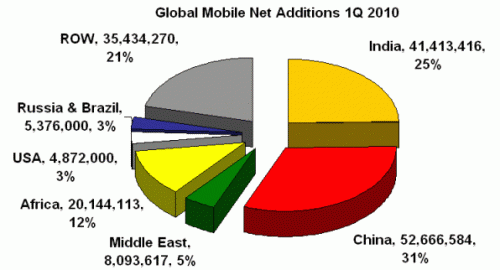
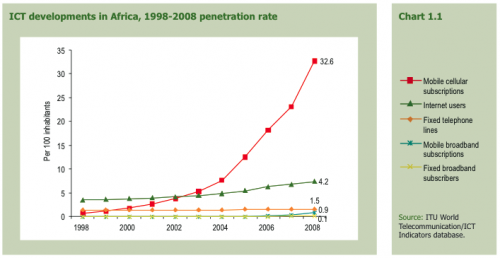
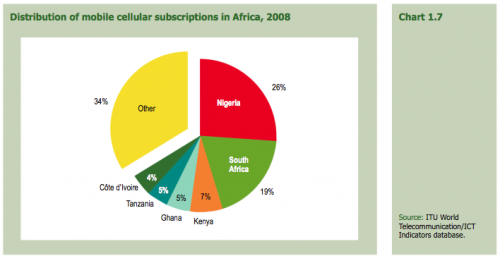
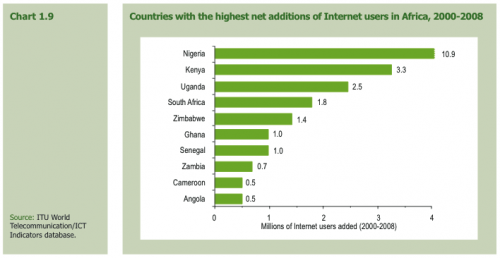
Vodafone recently concluded a policy paper on “Broadband in Emerging Markets”, also titled “Making Broadband Accessible for All“.
The position and reason for this paper is best summarized below.
“The success story of mobiles in the developing world is well known. Yet in the case of extending data services in emerging markets, there is a real danger of some serious policy mistakes. As in developed markets, broadband strategies in developing countries have tended to focus on investment in fibre. This is too simplistic. This focus on fibre may miss an opportunity for a transformational change built on the capabilities and in particular accessibility of mobile broadband. The early evidence suggests that mobile internet is spreading as quickly, in some developing countries, as mobile telephony did originally.”
Traditional definitions of broadband have a narrow focus on bandwidth and speed. This paper uses a wider definition, as broadband policy needs to consider the entire ‘eco-system’ of internet and data services from both a demand and supply-side perspective.
Content Sections
- Mobile Internet usage and demand in Kenya: The experience of early adopters (David Souter)
- The potential of mobile web content in East Africa (Erik Hersman)
- Spectrum policy and competition in mobile services (Thomas W. Hazlett)
- Rethinking mobile regulation for the data age (Martin Cave & Windfred Mfuh)
- Building next generation bradband networks in emerging markets (Luk van Hooft)
The Diffusion of the Mobile Web Across East Africa
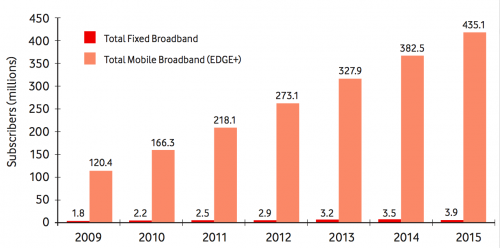
Mobile web content is growing at an astounding rate. It rose 2.6-fold in 2010, nearly tripling for the third year in a row. Official Kenyan industry statistics show that mobile internet subscribers will grow by approximately 843% for the 12 months to September 2011.
What I like about papers like this is that I get to use words that normal people don’t use. I make a case for international content and platforms as “drivers of diffusion” of data across East Africa. That simply means that these platforms and content are helping to spread the use of data more deeply into the region, and allowing local players to get in at lower costs.
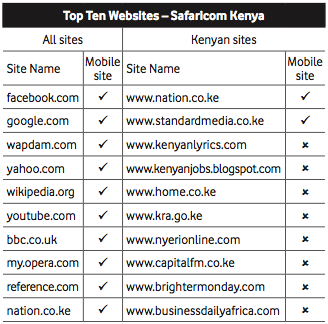 International web content is by far the most widely available and used in East Africa. This is in large part due to the ease of finding and disseminating this content, as well as its normalized licensing schemes and reliability. International platforms also carry a majority of the content that is currently being viewed on mobile phones. The following are the types of content that are most important to consumers in East Africa, according to our interviewees:
International web content is by far the most widely available and used in East Africa. This is in large part due to the ease of finding and disseminating this content, as well as its normalized licensing schemes and reliability. International platforms also carry a majority of the content that is currently being viewed on mobile phones. The following are the types of content that are most important to consumers in East Africa, according to our interviewees:
- International entertainment news (sports, gossip, lifestyle)
- Local news
- Breaking news
- Facebook (and to a lesser extent other social network tools such as Mig33, Mxit and Twitter)
- Jobs
- Dating (chat and relationships)
- Religion
- Local video/media
The reasons are that international platforms, such as Facebook, Yahoo!, BBC, CNN, Google and Wikipedia, have already been tailored to work on the most widely used data- enabled handsets. This contrasts with local content providers, many of whom have yet to tailor their websites for mobile access. In addition, local content less available at present, not as easy to license, and often cannot be reliably guaranteed as a long-term source.
Local Content
I interviewed a number of executives from Kenya, Uganda and Tanzania. There was a clear belief that while international content, increasingly localized for the market, is currently king, local content has the greatest growth potential because it is more highly valued by consumers.
While local content developers lack scale they have advantages that the global platforms do not. For one, they understand the local tastes and culture so customers value their content more. The consumer benefits of truly local content and platforms could be large.
The Government Role
There is still a lack of concrete government policies for government services or content to be made available or accessible via the mobile in any country in East Africa, even though this is the primary channel by which citizens could access services online. There is a solid case to be made for mGovernment, instead of just eGovernment.
To underline this, the most popular Kenyan Government website (Kenyan Revenue Authority) is shown as seen on a PC screen, a smartphone (HTC Desire) and a typical 2G internet enabled handset (Vodafone 350). The website is most clear and easily accessible via a PC interface (and consumer interaction primarily is through downloadable pdf files). There are no browsing problems when accessing through a PC-based browser. The KRA website is also accessible via the native Android browser in the HTC Desire Smartphone. The HTC Desire also allows downloading and viewing of pdf files. However, the native browser on the Vodafone 350 (a basic 2G EDGE handset) does not present the KRA website in a usable format. As can be seen, the website is badly rendered and quite impossible to navigate.

Possible government services to be made available via mobile web:
- Paying bills
- Service delivery questions and concerns
- Taxes – access, information and filing
- Health – access or appointments, information
- Public job search
An argument can be made that m-government services would have a greater impact if the focus were on supplying tools for small businesses to interact with government, rather than only making services available for citizens in general. By removing the barriers to entry for small businesses, the government would be providing a service that increased usage, decreased business costs and had a potential tax revenue increasing effect due to filing and paying on time.
Summary
East Africans are accessing the web primarily through their mobile phones. The new medium is enticing them online with the new services and content provided through a new medium. Broadband penetration rates are low enough in this region that we are not yet seeing the displacement of newspapers, radio and TV seen in other, more connected regions of the world. However, as with all network technologies, there is the potential for reaching a tipping point. This will depend on the provision of enough mobile web content that is valued by East African consumers.
The content driving East African users online is currently largely provided by international news and content sources, such as Yahoo! and the BBC, and also by global internet platforms, such as Facebook and Google’s Gmail. Even taking into account the decreasing data costs, falling data-enabled handset costs, and the increased availability of broadband, there would not be enough traction locally to get to the critical point if the content were not available.
These international content sources and global web platforms generate demand, and therefore allow the mobile network operators to decrease costs as more users come online. International content is thus providing a pathway for local content creators. While local content is in high demand and there is a rapidly increasing user base, the mobile web content space in East Africa is in its early stages, and there are no
clear leading content providers. At present the key trend is the provision of increasingly localized content by the leading global companies.
This paper has identified two important barriers to the further diffusion of mobile internet usage across East Africa: lack of m-government policies; and, more important, an absence of charging mechanisms which share the cost of mobile internet access between end-users and content providers. If governments embraced mobile-based provision of services and provided access free of usage charges to end-users (sharing the efficiency gains through payments to network operators), the potential impact on internet access could be dramatic. The challenge for governments and local developers of mobile web content is to utilize their local cultural understanding and ability to maneuver quickly to make their content more relevant and affordable to end-users.
(Note: This is summary of my section. Download the full 2Mb PDF report to read the section in its entirety, and to read the other 4 sections of the paper.)




 International web content is by far the most widely available and used in East Africa. This is in large part due to the ease of finding and disseminating this content, as well as its normalized licensing schemes and reliability. International platforms also carry a majority of the content that is currently being viewed on mobile phones. The following are the types of content that are most important to consumers in East Africa, according to our interviewees:
International web content is by far the most widely available and used in East Africa. This is in large part due to the ease of finding and disseminating this content, as well as its normalized licensing schemes and reliability. International platforms also carry a majority of the content that is currently being viewed on mobile phones. The following are the types of content that are most important to consumers in East Africa, according to our interviewees: