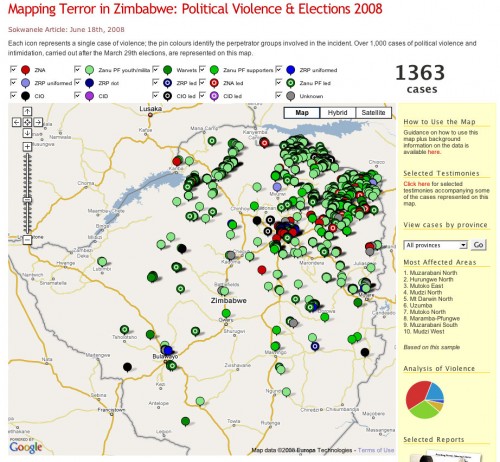
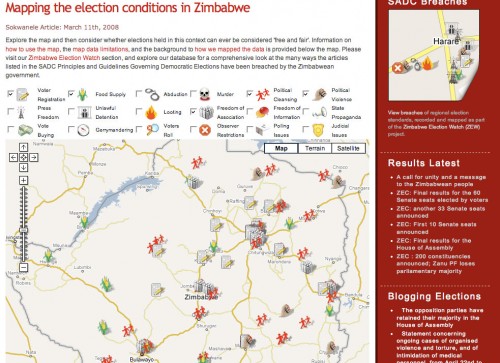
A scotoma is a blind spot in your vision. Everyone has it, and it’s due to the lack of photoreceptors where your optic nerve exits your eyeball. Normally, it’s right at the center of your vision. It’s curious to note that most maps have Africa placed squarely in the center, and most are blind to it as well.
A scotoma is a blind spot in your vision. Everyone has it, and it’s due to the lack of photoreceptors where your optic nerve exits your eyeball. Normally, it’s right at the center of your vision. It’s curious to note that most maps have Africa placed squarely in the center, and most are blind to it as well.
I’m a big fan of infographics, visualization tools that help us understand something faster than reading a long-winded explanation or a spreadsheet of data. It’s disappointed to see how Africa is usually missing from the global ones – especially in relation to technology.
I call this “Africa blindness”.
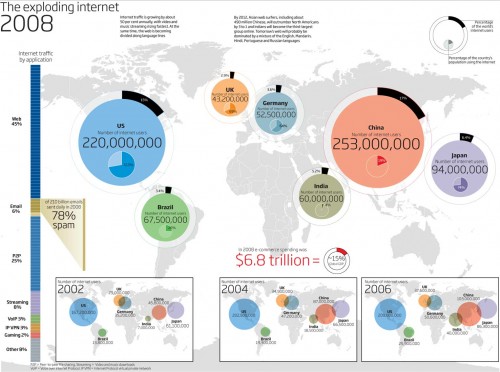
Luke Wertz linked one to me earlier today from the New Scientist on Twitter saying, “Notice anything missing from this image? Oh yea, the ENTIRE continent of Africa.”:
It’s a good graphic, really well designed and it does gets a point across. However, it’s missing two continents: Africa and Australia. Thank goodness, we’re not just dealing with Africa-blindness, but Oz-blindess too. 🙂
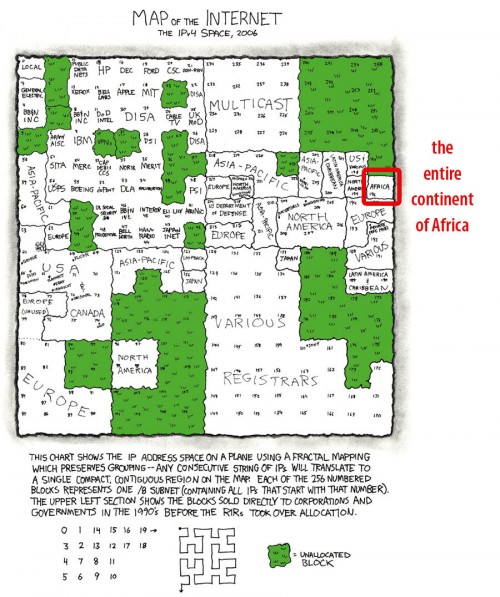
Here’s another great technology infographic, this time by XKCD where he’s showing the IPv4 space (that’s how you get an IP address). Note the glaringly obvious fact that the entire continent of Africa has the same-sized IP allocation as the likes of Apple and half as much as Japan.
Is there a case for Africa Blindness in tech?
A part of me can understand how a graphic designer sitting in the US or Europe, tasked with creating a graphic, would bypass Africa. After all, if you’re not from the continent, you surely don’t think of it as having much relevance in the high-tech world. On top of that, it’s not always easy to find web and mobile data in Africa as it is in the rest of the world. The first is an issue of education and media focus. The second is far more serious of a problem.
You’d think that finding aggregate information on tech in Africa would be fairly easy to find. It’s not, at least not for free like it is for much of the rest of the world. If anyone should know this, it’s me. After all, this is what I spend a great deal of time tracking…