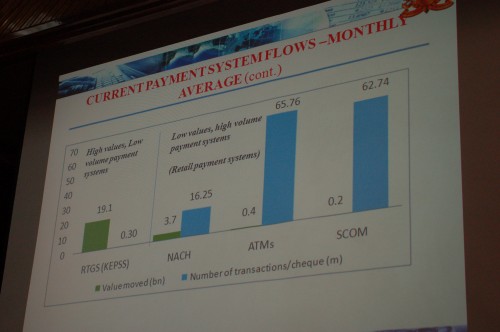
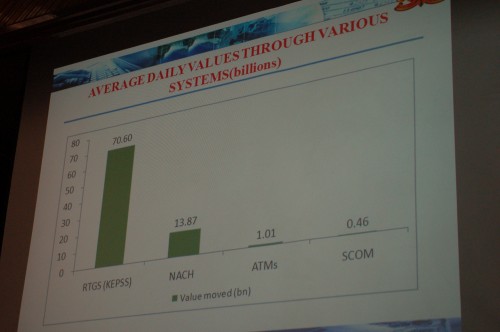
I’m attending the Fletcher mBanking conference in Nairobi today and tomorrow. Right now I’m sitting in the panel on “Perspectives on Mobile and Branchless Financial Services”. It’s quite a panel with, among others, Michael Joseph of Safaricom (of Mpesa fame), Adan Mohamed of Barclays Bank, David Proteous of Bankable Frontier Associates.

Points from the Panelists
David Porteous
He challenges Kenya to create a Kenyan model, not just of one-off success stories, but a Kenyan one that is open and usable by multiple actors in the country, not just one or two. Something that can be duplicated and used around the world. Lastly, he warns of “Regulator Flu”, much like Swine Flu it sweeps around the world and stifles innovation.
Adan Mohamed of Barclays
Adan starts with this provocative statement, “We will never have an environment where we have no branches.” He says it is ingrained in our psyche to use branches, and we will always need branches, so this idea of a branchless banking system is nice, but will run concurrently with the old status quo system. The use of technology continues to be small, it’s patchy, it’s mixed. There’s a long way to go, as people are nervous of what goes on behind this internet system.
Specific challenges revolve around regulation. For instance, if you want to run it 24/7, you have to get permission, you have to deal with money laundering rules, etc… He thinks that the central bank needs to be given a greater mandate. However, we need to see this space not revert back to the old ways, even as more control is given.
Customer contact tends to be low in a branchless system. He thinks this is a place where people want to be in touch and face-to-face with people. A lot of focus has so far been on the payment side of the occasion – we need to focus on the savings side of the equation as well.
Mark Pickens of CGAP
What we have today, is not necessarily what things will look like in the future, “what could disrupt the current landscape?” Mobile network operators are leading the charge. We think there will be 120+ initiatives like Mpesa in the next year around the world.
What is driving this for the mobile operators?
- 2.93B shillings from Mpesa of revenue
- Increases in loyalty
- Increases in users
- Globally think there is 1b ppl with a mobile phone but no bank account
Where else could innovation come from?
What if the kinds of technology that poor people had in their hand changed dramatically? If the phones that people had in their hands could browse the internet. Not smart phones, but sub $100 phones for this.
- Why would this matter?
- GPRS and EDGE are dramatically cheaper than SMS (75x cheaper)
- Mobile operators and banks would not own the customer due to owning the infrastructure. Anyone could reach out and find customers directly. The incumbents wouldn’t be as privelaged.
Localized creation of tools
3 main points:
Regulation. Particularly openness for non-banks to operate. Would there be a regulatory framework where this could be open for others to access and bes safe operating within? If we think that banking infrastructure needs to be openly accessible, then what is needed in the openness of mobile infrastructure?
Agents. The preponderance of Mpesa agents make a profit of $5/day. If there is limited capital in these dukas and agents, then how will he get liquidity to do it for anyone else? Maybe it can be done by extending lines of credit to the agents.
Consumers. The next round of innovation is beyond payments, but to use the wallet to store value. Who are the players that can provide this service on a safe basis? Paying for products directly would cut the cost for agents directly, and it would cut the cost of money within the system to the gov’t (2-3% of GDP). Poor people do have money, and they do save, but they put it at home in a jar, under the matress. What comes next innovation, is that the mobile needs to beat the matress
Peter Rinfretof Iris Wireless
Friction will continue to increase between operators, banks and other institutions like Western Union, etc.
The regulations and regulatory environment will change a lot for everyone. You’ll see regulations in one country that affect other countries. His example is the US is the largest remittance market in the world, and that has huge repercussions to what happens in the other countries around the world. Anti-money laundering rules will become stricter and more difficult for receiving countries to comply.
We’re not talking about a change of habit that is relatively new. This is money, something we’ve been dealing with for millenia. We’re talking about old habits dealing with money, so it will take time and it will evolve slowly. And it has to make sense within the market that you’re in. No two markets will look the same.
Michael Joseph of Safaricom
Mpesa launched in March 2007. It’s surprising to see how fast it’s grown. 19% of the population is banked, but 71% who have access to mobile phones in Kenya. The key success of Mpesa is not just good working technology, but to be successful with it you need to understand distribution. It’s not cheap. It’s not easy to put together an agent network that operates with integrity. “It is not build it and they will come.”
Customer growth is at 6.2 million customers in March of 2009 with over 11,000 new registrations each day. Trends: $1.7B moved in P2P transfers since launch. Average P2P transaction is just under 2500/= shillings ($30).
“This is what worries the banks, that we’re moving all this money around and they’re not getting any fees.” We’re not a competitor to banks, because they couldn’t operate on these small 30/= fee.
Safaricom has 300 staff dedicated to Mpesa. There are now over 10,000 agents. It’s the McDonalds effect” – whenever you are hungry there is a MacDonald’s. For us, whenever you turn around there is an agent.
“It is so important to have a regulator that is willing to take a risk with you.” It took nearly 9 months to convince the regulators in Kenya to allow them to launch Mpesa. We are treading new ground in Kenya, so having a courageous and risk-taking regulator made it possible. For money transfer we need some sort of regulation – a level playing field for others to do this a well. Regulation should facilitate and not frustrate.
“When we look back, money transfer will be the biggest thing that we ever did in the telecommunications world.”
 Ken Njoroge is a homegrown Kenyan technology entrepreneur. One of the original founders of one of Kenya’s top digital agencies, 3Mice, he moved on to co-found Cellulant, which has been doing some great work all over East Africa and is now active in 9 countries in Africa (Kenya, Tanzania, South-Africa, Ghana, Rwanda, Botswana, Zambia & Ethiopia).
Ken Njoroge is a homegrown Kenyan technology entrepreneur. One of the original founders of one of Kenya’s top digital agencies, 3Mice, he moved on to co-found Cellulant, which has been doing some great work all over East Africa and is now active in 9 countries in Africa (Kenya, Tanzania, South-Africa, Ghana, Rwanda, Botswana, Zambia & Ethiopia).