India is watching Africa closely, especially after the big $10.7bn move by Bharti Airtel to take over Zain’s Africa operations. Yesterday Ankit Rawal, head of advertising for inMobi in Africa, spoke at the iHub. He spent a good amount of time explaining why Africa was so important to their growth strategy, and used a good bit of data from an InMobi research project to show why.
Ad Impressions
From their July 2010 statistics, Africa has over 2.8 billion mobile ad impressions available, an 18.5% growth from just one month before (June 2010). That’s an amazing figure, and amazing growth, by anyone’s standards. Only 16% of that inventory is on smartphones.
InMobi’s largest African markets, in order, are: South Africa, Egypt, Kenya, Sudan, Libya, Nigeria. There is a big difference between these countries and some of the others that we saw stats for. For instance, Mozambique, Tanzania, Angola and Namibia have only about 20-40 million impressions/month. There is a wide gap between Africa’s tech leaders and the rest of the continent.
Manufacturers
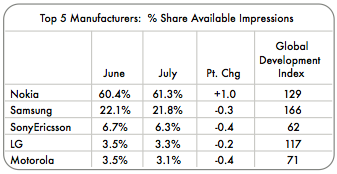 Continent-wide, the most popular manufacturer is Nokia at 61.3%, followed by Samsung at 21.8%, with SonyEricsson a distant third at 6.3%. Those aren’t especially surprising figures, but if you dig down into the country details provided for South Africa, Kenya and Nigeria, they differ.
Continent-wide, the most popular manufacturer is Nokia at 61.3%, followed by Samsung at 21.8%, with SonyEricsson a distant third at 6.3%. Those aren’t especially surprising figures, but if you dig down into the country details provided for South Africa, Kenya and Nigeria, they differ.
- In South Africa, it’s 38% each for Nokia and Samsung
- In Kenya, it’s 66% Nokia and 18% Samsung
- In Nigeria, it’s 78% Nokia and 9% SonyEricsson
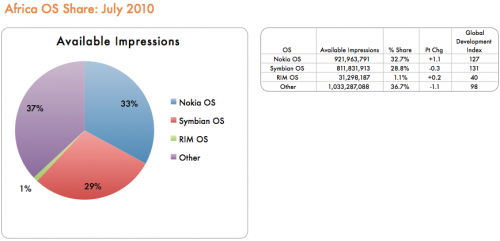
Operating Systems
Important information for mobile app developers and businesses is which operating system to focus on. Nokia OS and Symbian lead, followed by RIM. No Android, iPhone or Windows Mobile mentioned, though there is a suspiciously large (37%) chunk of the pie for “other”.
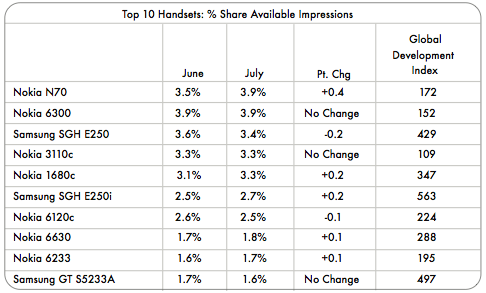
Handsets
The actual devices that people are using that show mobile advertising is interesting as well. It’s largely Nokia, holding 7 of the top 10 spots, with Samsung carrying the other 3. The top device, is the moderately priced Nokia N70 is a popular, though unpretty, “do it all” phone.
Other Information
Not available in the qualitative research document provided by InMobi, but part of Ankit’s talk yesterday, were some other demographic statistics.
Male acceptance of mobile advertising in Africa is the highest in the world, when asked, “How comfortable are you with mobile advertising?”. African women came in second behind Asia on that same question. Women in South Africa were the clear outlier compared to Nigeria and Kenya, with only 45% comfortable with mobile ads.
Africa’s under 25 population has the highest comfort level with mobile ads in the world. 75% from this age range are okay with mobile ads, as opposed to 67% in Europe, 73% in the US and Asia.
South Africans are more interested in ads when top global brands appear as ads. The primary benefit of mobile ads that all consumers are looking for is “new information”.
Final Thoughts
Africa, as a whole is well positioned to see a huge growth in mobile advertising. This comes from a combination of consumer acceptance of mobile ads being the highest in the world, healthy support via increased data plan competition among telcos, growth in 3g and smartphone adoption, and mobile screen mindshare amongst users.