[This post is my talk from NetProphet 2010 in Cape Town, South Africa. Keep in mind it was aimed at a crowd that was close to 100% South African, and my purpose was to show what was going on north of the South African border.]
The idea for this talk came from a conversation that I had with a programmer that I met in Jo’burg when I first visited 3 years ago. After a talk that I gave, he told me, “Someday I’d like to visit Africa.” As you can imagine, I wasn’t quite sure how to respond.
Now, I think he meant this Africa

I would rather speak to you about this Africa
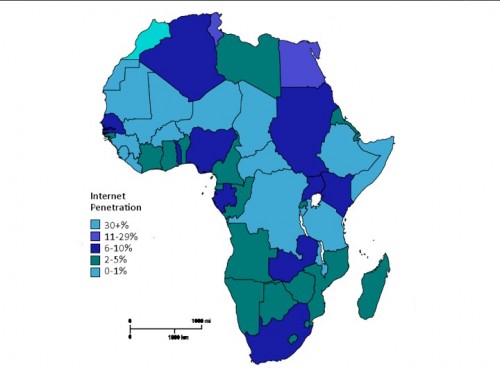
This map color codes countries by their level of internet penetration. As you can see, all of Africa has a fairly poor internet penetration rate compared to the rest of the world.
South Africans sometimes forget that they are a part of a much larger continent, choosing to align themselves closer with far-away Europe than their bordering countries, and they miss all types of opportunities due to this.
So, when Tim asked me what I wanted to talk about at NetProphet this year, I thought it a great opportunity to highlight some of the entrepreneurs and opportunities that lie just north of this great country.
Most of us look at this map and say, “that’s pathetic”. A few say, “blue ocean”, a completely untapped market ripe for the picking.
I’d like to start off then by telling you about two people, Karanja and Fritz, who are of the latter type, and they’re making good money working in this market. First mover advantage in the tech space has always been a key, and their early inroads into the space position them perfectly for taking advantage of a growing mass of consumers.
A story of 2 entrepreneurs
Karanja Macharia is the founder and CEO of Mobile Planet, a mobile company in Kenya that provides third party services to both the main mobile providers and other corporate clients. They’ve been around for a number of years, Google invested in them 2 years ago, and most importantly, they’re profitable.

I carry around a Nexus One and an iPhone. Karanja carries around a Nokia 1600, the cheapest data-enabled phone you can buy ($25). Why? He does this so that he understands what his customers need and use. His clients aren’t your upper-class Blackberry toting professionals, they’re the “wananchi” (the ordinary person).
It takes a paradigm shift in the understanding of people, culture and spending habits to tackle this market. It’s not a population that understands the PC-web in the same way that you, me or anyone from the West does. It takes a different perspective, and a different type of entrepreneur.
In Kenya, approximately 40% of mobile users don’t keep a balance on their mobile phone. This means, they might top up with 10-20 Ksh from time to time to keep their phone active, but most of the time they have the phone for people to call them. At the same time, there’s a burgeoning opportunity and demand for mobile web content. So, the question is, how do you get that 40% active on the web with the current pre-paid model in Africa, where everything has a cost?
Talking to someone like Karanja is an eye opener, you quickly realize how deftly he wields his knowledge of mobile consumers in Kenya against the realities of the mobile operator’s business culture and the “freemium” pricing of the web as it too grows in penetration here.
Karanja represents this new technology entrepreneur in Africa. He’s a seasoned businessman, not some wet behind the ears University student. Karanja understands cash flow and business management, as well as the differences between a PC-web based culture and the mobile-base culture that is sub-Saharan Africa.
_______
Fritz Ekwoge is the founder of iYam.mobi, he too comes from a professional background, though as a programmer and developer, not pure business. He represents a different type of entrepreneur, a younger generation that knows and cares about the web world beyond his Cameroonian borders, and tries to figure out how the two can work together.

Last year I wrote about his first application, iYam.mobi, which is a mobile phone based mobile directory. It works off of the assumption that no one using it ever touches a PC and therefore won’t need it when they look for contact information of service providers via an SMS command to the server. It’s simple, and it works. Fritz has taken the original iYam.mobi ‘mobile mobile’ directory concept and run with it. It’s evolved into a generalized SMS-based content publishing platform with virtual currency that anyone can use to create and consume local content services.
That application has been rewritten and is now onto another application that might be even more interesting. Fritz has created a new SMS Apps Store at iYam.mobi, and his company has been named FeePerfect. Fritz is in the process of obtaining his VAS (value added services) license. The platform is undergoing testing and will be released as private beta next month.
Fritz represents this new technology entrepreneur in Africa as well. He’s done his time at firms like PriceWaterhouseCooper, sees the digital landscape both internationally and in Cameroon, and realizes the opportunities available in his home market that are difficult for outsiders to bridge.
Many people claim that, “the future isn’t SMS” with too many limitations and a horrible cost structure. That might be true. However, it’s also the present reality. What Fritz understands is that you build for what people need, not for what tech pundits in the West and upper class Africans idealize about.
Why do these stories matter?
Both Fritz and Karanja come from completely different backgrounds. Business, culture and technological penetration vary greatly between Cameroon and Kenya. In one, you’re not surprised to hear of entrepreneurial success and innovative thinking while in the other you do wonder about the consumer-side viability of mobile or web-based products.
I believe these stories are important because they take us outside of our comfort zones. We are forced to come to the realization that our understanding of the business potential of technology entrepreneurs in Africa is far greater than we had thought. We consistently underestimate the viability of consumer markets in Africa because we do not truly understand the customer there.
One other point I’d like to make on entrepreneurs. Justin Spratt wrote an excellent piece on the new Memeburn site, called “10 Lessons for Founders“. In one of his last paragraphs he talks about the Ideal Founder. All of these same traits are clearly visible in the new tech entrepreneur in Africa, so they’re not that different than their Western counterparts on a personality level. Where they do differ is in their understanding of how to bridge their culture and technology.

Where is it happening?
There are a couple major cities that act as hubs for technology innovation in Africa.
- Johannesburg and Cape Town in South Africa
- Nairobi, Kenya
- Accra, Ghana
- Lagos, Nigeria
- Cairo, Egypt
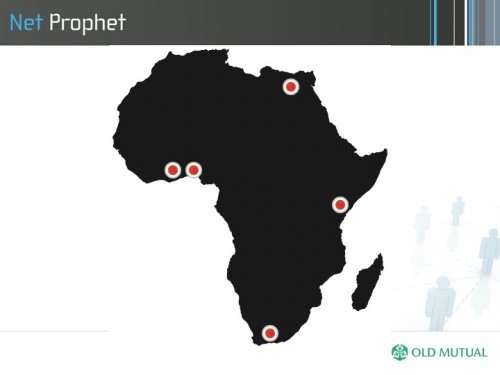
Looking at maps like this and talking to individuals in this space, I tend to disagree that the digital divide is primarily between rich and poor in Africa. My theory is that it’s more urban versus rural than anything else. I do travel quite a bit, and I’ve found that you’re much more likely to see a data-enabled phone in use in the slums of Kampala than in the rural backwoods of Liberia.
These cities are the ones to continue focusing on and encouraging a critical mass of programmers, businesses, universities who focus on tech and funds and investor groups to formulate.
One of the projects that I’ve been heavily involved with since the beginning of the year is a new tech innovation hub in Nairobi, called the iHub. Our goal is to create a nexus point for the tech community in Nairobi.
It’s an open space for the technologists, investors, tech companies and hackers in the area. This space is a tech community facility with a focus on young entrepreneurs, web and mobile phone programmers and designers. It is part open community workspace (co-working), part vector for investors and VCs and part incubator.
I’m firmly of the belief that spaces like the iHub in Nairobi, Limbe Labs in Cameroon, Appfrica Labs in Uganda, Banta Labs in Senegal , and a new Geekspace here in South Africa (where there are more) are just the types of place that we need to get behind. These are the places that draw in the interesting people and projects, and they also serve as a filter and trusted intermediary for outside investors and businesses.
Thus far we’ve only seen the first generation of mobile and web entrepreneurs. There are a few good successes stories, but not enough. What these cities represent, and the hubs within them, is a space for that next generation of entrepreneurs to rise up. Locations to look for the newest and best ideas, invest in them, and then help them grow beyond the urban boundaries that pen them in right now.
Finally
Still don’t believe that the Africa north of you is worth taking a look at?
“Kenya is proving more lucrative per subscriber than South Africa for mobile advertising.”
Hearing someone tell me that, from one of the leading mobile advertising networks, was surprising. But, I’m guessing not nearly as surprising for me (who lives in Kenya) as it probably is for you, who live in South Africa.
We have a rising tide of technology beating against our continent’s shores, and it comes as no surprise to me that we have entrepreneurs rising up to meet it.














