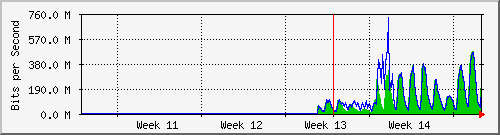
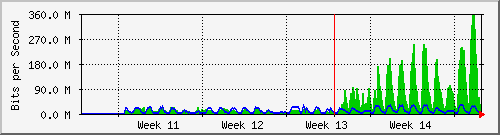
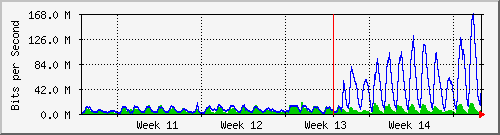
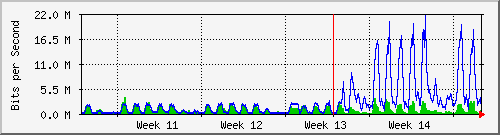
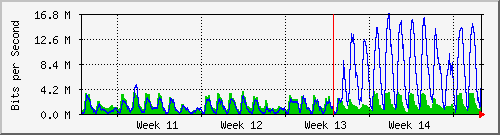
99% of Kenya’s 6.5m internet users access it via mobile, of which Safaricom owns 77% marketshare.
In Kenya, when you buy a 1.5Gb internet bundle from Safaricom you pay 1000ksh (~$12). You’ve paid for the data, and there is no additional cost to Safaricom if you were to use that data today or a year from now. The whole concept of data bundle expiry is ridiculous, as noted by Safaricom CEO Bob Collymore when he visited the iHub:
“When you go into a petrol station and fill up your car, does the owner of the petrol station tell you to bring it back on Wednesday to take back what’s left in the vehicle? Of course not. So I ask, why the hell are we doing that?”
Bob goes on to say that he isn’t going to be an apologist for this practice, that there is a problem with leaving the data there ad infinitum. That 60 days is probably too short and that Safaricom does need to change how they handle this.
- Until recently they just held your data hostage. If your data expired, you could recharge with just a few shillings of data, this would re-trigger your “old” data that was past the expiration, and have that available to you again.
- Today, it is “data gone, money stolen” after expiration. They cut you off if you haven’t used all of your internet bundle in the nominal 7-90 days, no matter how much is remaining.
I brought this up with Bob Collymore, and his chief executives when they visited the iHub earlier this year (see video), at which point he admitted that it was indeed a dubious practice that would be changed to something much more open to users. You’ll see what Bob says at the 1:17 mark in the video below.
Here Bob is on video speaking to this point (I’ve saved the link to go to the right point in the video):
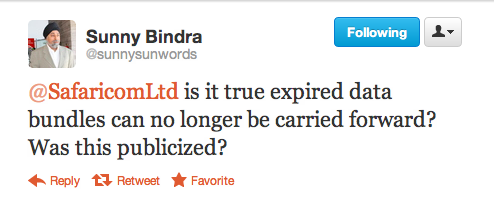
The other day I caught a Tweet from Sunny Bindra about some surprising changes:
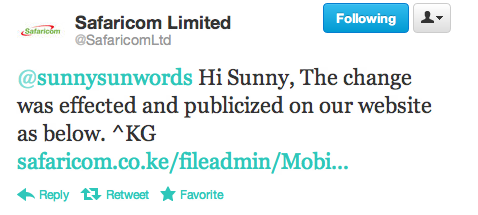
Safaricom is actually very responsive on Twitter, probably the best big company on social media in the Kenya. They followed up with Sunny with this:
So, Safaricom didn’t broadcast this significant change in the way data bundles are handled broadly. Apparently, “publicized on our website” means quietly posting a PDF somewhere in the morass that is their website to notify the data using public of the changes.
If you follow the links to the PDF, you’ll find the following:
What is the Validity period?
This is the time frame that you have to use the bundles, when this period elapses it means that any remaining bundles will have expired and will not be available for use.
(Note: there is conflicting information on how long bundles will last, you can only find out by topping up a bundle. I did this for 1.5Gb and found that it’ll last 80 days, not the 30 that they say in the PDF. I don’t know if it’s more/less time for other bundle amounts.)
It’s in Safaricom’s best interest for you to keep buying more data, over and over, even if you haven’t used it. It costs them nothing to let you use it over a longer period of time, or to keep recharging it.
In Conclusion
I’m disappointed with Safaricom, especially after Bob Collymore came to the iHub and said he was going to fix this, not break it further.
This is an outright fleecing that the Safaricom team should be questioned on. In a country where they are the monopoly player on the primary source for people to access the internet, this makes them appear like a bad actor.
Basically, we’ve gone from a bad system that was promised to be made better, but which had a corrective option, to a worse system that has no option.
Other Safaricom Data Miscellany
While I’m at it, let’s go ahead and talk about a few other ways that the data service that Safaricom raises the bar for bonehead usability: buying data bundles themselves.
Case 1:
 You used to be able to send airtime to a SIM card on your Safaricom modem. Then, using the inbuilt Safaricom Broadband app, send an SMS to 450 with the amount of the bundle that you wanted to buy, now 450 only seems to work for checking your balance.
You used to be able to send airtime to a SIM card on your Safaricom modem. Then, using the inbuilt Safaricom Broadband app, send an SMS to 450 with the amount of the bundle that you wanted to buy, now 450 only seems to work for checking your balance.
With the new service updated in the aforementioned PDF you can now only use the USSD code to update it.
Solution now?
Take the SIM card out of your modem, load it in your phone and do the USSD code. Once confirmation is received, switch that SIM card back to the modem.
Yes, that’s correct. Instead of being using the software that comes native with your modem, you now have to use a phone to update your bundles. Why would you change your system to not work with everything that people use? I’m quite curious actually. I can’t understand this decision from a either the business or the product side at all.
Case 2:
Safaricom wanted to make it easier for people with modems, iPads, Android tablets and smartphones to be able to update their bundle (good idea). They created http://portal.safaricom.com/bundles for this purpose. Let’s say you’re out of data, you have no credit on your phone. How do you get to this page?
Solution?
There are none. You’re stuck because this page isn’t zero-rated. This is mind-boggling in it’s oversight. I have no data, therefore I cannot go to your page to load more data. Seriously… who is the genius that thought this up? Or, probably more accurately, what form of bureaucracy is in place that allows this mediocrity to persist?
Further, if you’re Safaricom who controls 77% of the consumer internet access in Kenya, why wouldn’t you zero-rate your whole Safaricom.com domain and make it free for anyone to surf, even if they don’t have a single shilling on their phone?
[As a resource, here is the latest quarterly Communications Commission of Kenya (CCK) PDF report on the tech scene in Kenya.]



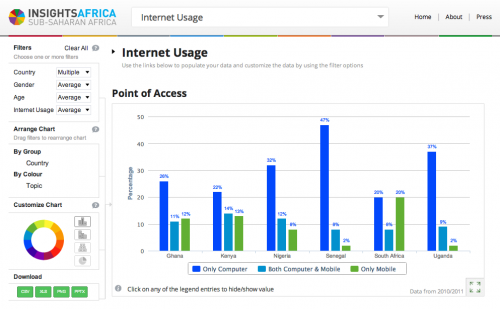




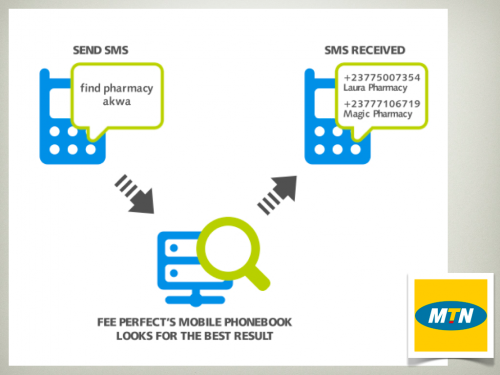


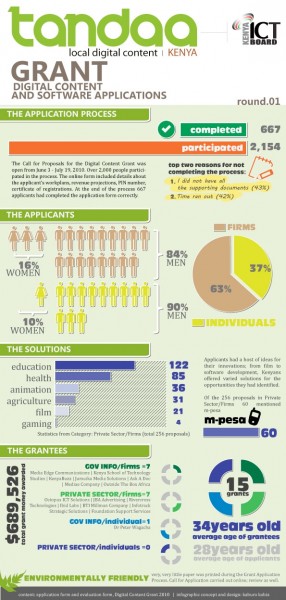

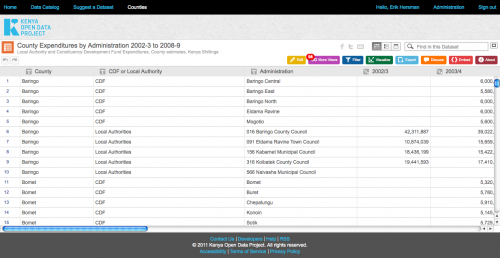
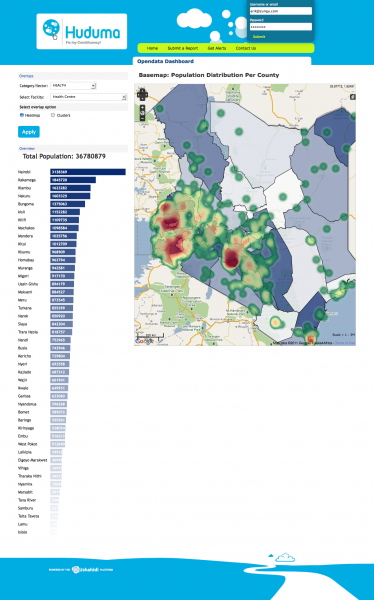
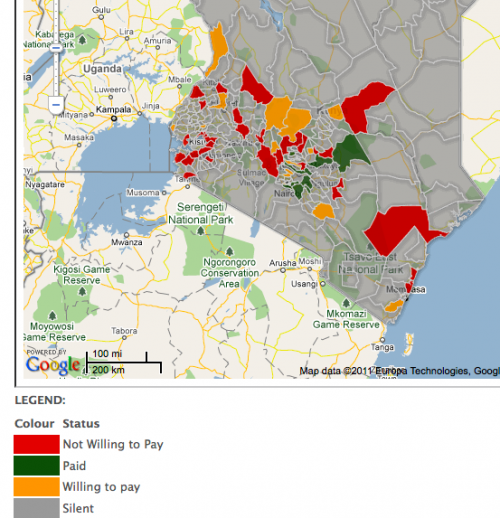
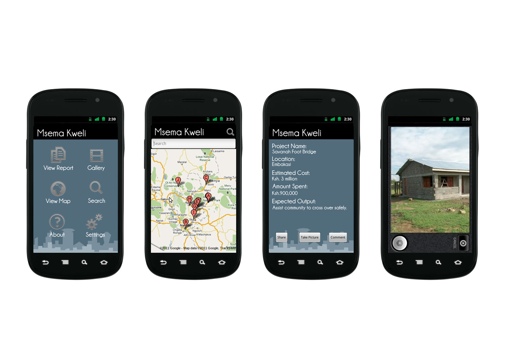
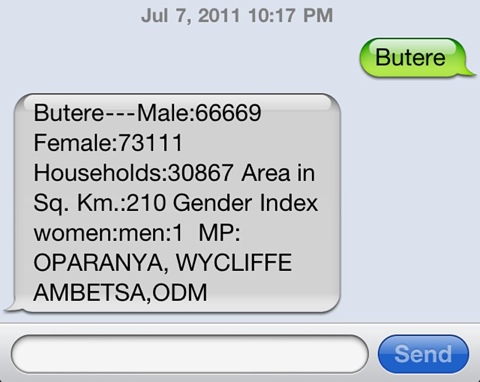
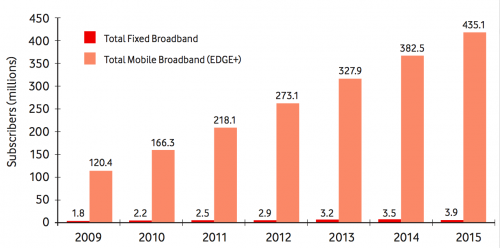
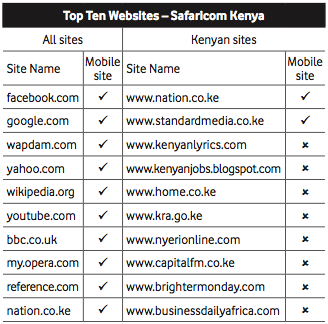 International web content is by far the most widely available and used in East Africa. This is in large part due to the ease of finding and disseminating this content, as well as its normalized licensing schemes and reliability. International platforms also carry a majority of the content that is currently being viewed on mobile phones. The following are the types of content that are most important to consumers in East Africa, according to our interviewees:
International web content is by far the most widely available and used in East Africa. This is in large part due to the ease of finding and disseminating this content, as well as its normalized licensing schemes and reliability. International platforms also carry a majority of the content that is currently being viewed on mobile phones. The following are the types of content that are most important to consumers in East Africa, according to our interviewees: