This year at Pivot East I had my first look at Sendy, which does for motorcycle courier deliveries and customers in Nairobi, what Uber did for taxis and passengers in San Francisco. At its heart, Sendy is about bringing the vast and growing motorcycle courier and delivery network in Africa into the digital and networked world.
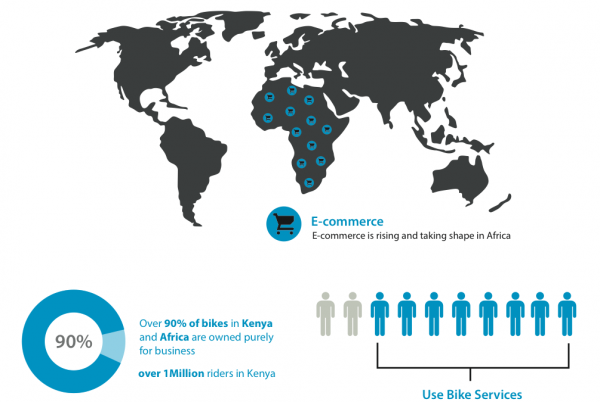
This is a big deal, because those of us who live in large African cities know just how inefficient driving a car around the traffic-plagued metropolises can be. With the bad roads, traffic and high cost of fuel, motorcycle deliveries are a natural path.Indeed, in almost every city, from primary to tertiary throughout the continent, you’ll find thousands of motorcycle guys sitting by the side of the road, ready to courier a package or serve as a taxi. They ride inexpensive $800-$1200 Chinese and Indian motorcycle brands, are generally not trained very well, have little safety equipment and are some of the most reckless riders I know.
When Alloys Meshack, Sendy’s CEO, stepped onto stage for his 7-minute pitch, I was hooked. It sounded like the right team, a good business plan, and one that could scale well beyond Nairobi. I met with him again this month, and got into a lot more details around the business, and this encouraged my thoughts on both him and his team, as well as the broader scope of the business that they are building. It is truly impressive.
How it Works
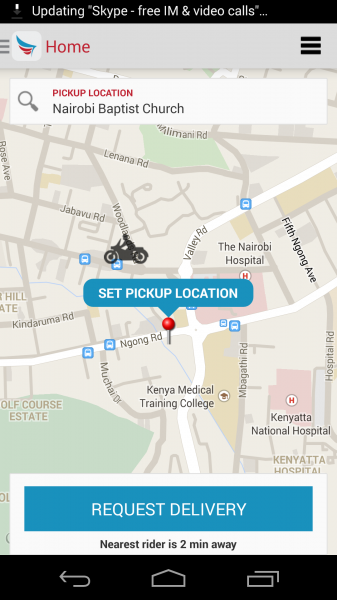
I also signed up for the service, and then used it.It’s as simple as this:
- Download the Android app, or sign-in to the web app at Sendy.co.ke
- Click the button that you have a delivery (or pickup) to be made.
- You can see the map for where the rider is – my wait was approx 5 minutes for the courier to arrive
- Give him the package and directions
There is a GPS transponder on the motorcycle, and you get an SMS update when the delivery rider gets withing 50m of the delivery zone. Once the package is delivered, there is another confirmation that the rider sends to Sendy, that comes to you as well. Payment is then made automatically by either credit card or Mpesa.
My delivery took about 25 minutes, from first Android app entry, to delivery about 5km away. At the end, you can rate your delivery rider, so that the best are known and get more business. I found my particular rider courteous and patient. He also told me that he makes about 5-6 deliveries a day with Sendy, and loves the service.
Challenges and Opportunities
With Africa’s growing need for logistics around eCommerce, Sendy presents a natural option for everyone from Jumia to your local supermarket. Motorcycles are already an accepted means of delivery for non-traditional business and large enterprises alike. The idea of capturing a large portion of this, without all the baggage of a normal courier company setup, is good for both Sendy and the everyday bodaboda/courier guy.
There are a couple hurdles to overcome to make this a simple process to onboard new customers, receive payment and then send payment to the courier riders. Unlike the US or EU, not everyone has a credit card, and the mobile payment options don’t allow for “pull” billing (instead, the customer has to “push” a payment to your service), which is clunky.
Sendy has corporate accounts (which is now used by both BRCK and Ushahidi), and for businesses, finding a good payment process isn’t a problem. However, there will need to be some creative thinking for individuals and small businesses in order to make Sendy as painless as it promises to be.
The service verifies the courier riders, keeping their records on file, and providing the necessary technology for both tracking of motorcycle and communications with the rider. This means that qualified riders are picked, lessening the chance of getting robbed, and the ability to rate a courier creates a system that builds trust over time.
The opportunities that Sendy represents are staggering. I encouraged Meshack to get Nairobi right quickly, then scale up and move beyond into other major cities in the region.
Sendy is raising a seed round of investment. If this opportunity is interesting to you, you should reach out to them.