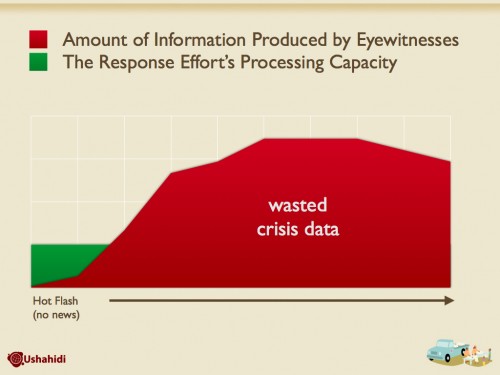
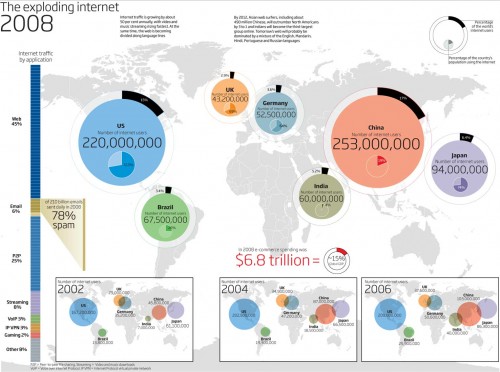
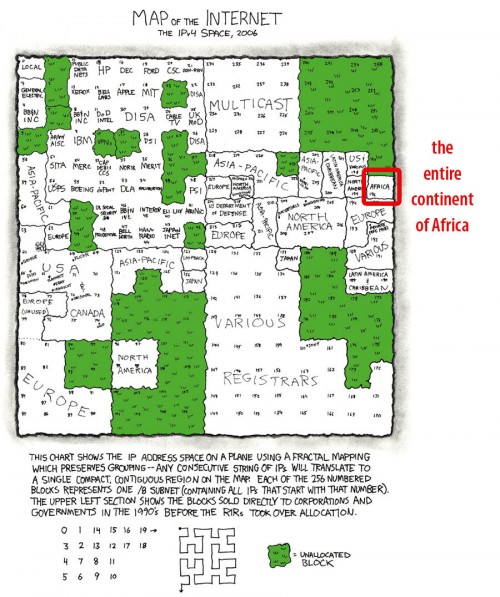
[The following is from my Institute of Medicine Talk on communications technologies for violence prevention in Washington DC today. A good background paper to get started on the context of tech in violence prevention is found in this PDF. ]
Something has changed over the last decade.
New technology is lowering barriers. For everyone, and everything. It is disruptive just by existing and by it’s penetration into every corner of the world. We’re talking mobile phones, social media, open data, inexpensive mapping and of course the internet itself.
It can be used just as easily for good as for bad, like any other tool and medium before it. However, the biggest difference in our new technology space, is that what before had at least some gatekeepers, now has few or none.
Inefficiencies in older industries or organizations are areas ripe to be disintermediated in our day of new tools and democratizing of information. Think big media, government, the humanitarian field and even the medical and healthcare industries. Many of these are centralized, top-down information systems which are being forced (or will be forced) to change, or become obsolete and die out in their current form. Not because what they represent is bad, but because how they do it is no longer viable.
Legacy systems and processes were built for a use case that is often decades, if not centuries, old. Internet and mobile phone technology bring new efficiencies and lower barriers. At the very least we can expect new technology to augment what’s there, if it doesn’t displace it entirely.
We’ve see this rippling through the media world for the past few years, large magazines and newspapers are going out of print, major TV networks are struggling. New technology is changing the news paradigm.
We see it in government, from fund raising to how wars are fought, and especially to how a faster moving populace interacts with a slower, archaic and sometimes rotten system that rules them. New technology makes a nimble adversary out of the people that the government is sworn to serve.
We see this in the humanitarian space, where large, slow and ungainly organizations can’t seem to coordinate the resources to meet their mandate, yet raise enough money to keep themselves in business. New technology allows the affected people to self-organize and solve their own problems, and leads us to question why some organizations exist at all.
Let me give you a finite example of this, from my own organization, Ushahidi.
Ushahidi was born out of the post-election violence in 2008. In that first week, a number of us came together as an ad hoc group of volunteers and in 3 days created a website that allowed anyone in the country to send in text messages, emails or web reports on problems happening in their area and we mapped them and put them on a timeline. It was simple, rudimentary even, but it worked.
It worked because people were looking for an outlet, they wanted to let people know what was happening to them.
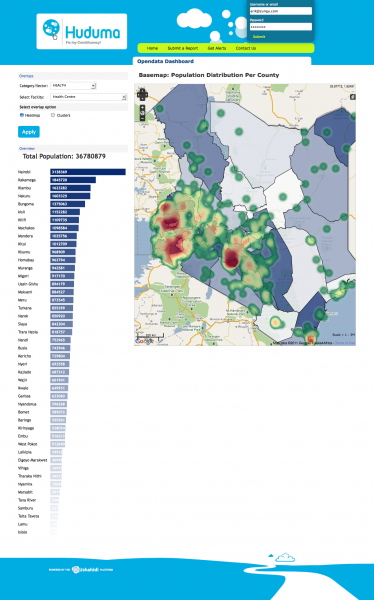
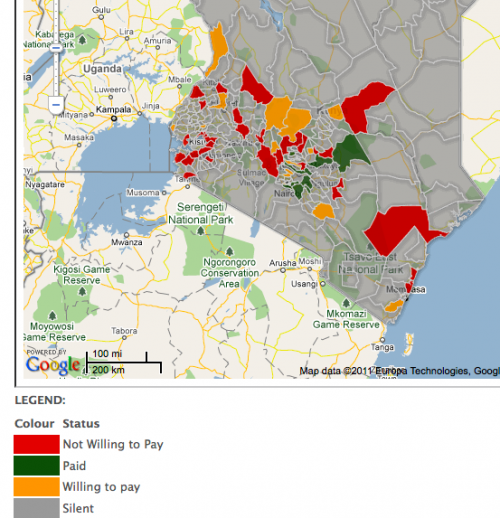
What we’ve seen since that time is that Ushahidi has proliferated, not because of the technology, but because of the use cases that it makes possible. It is a free and open source platform for gathering and visualizing information and it has been used for everything from disaster response to election monitoring, citizen journalism and community engagement.
There are now over 20,000 deployments of the Ushahidi platform operating in 132 countries. Our goals for Ushahidi are simple; to disrupt the way information flows in the world by providing the best tools for democratizing information with the least barriers to entry.
In the beginning this meant take what took us 3 days to build and make it available to others so they didn’t have to start from scratch. Something that would take them only 3 hours to deploy. Last year we dropped that to 3 minutes with the launch of Crowdmap, our cloud-based version of Ushahidi.
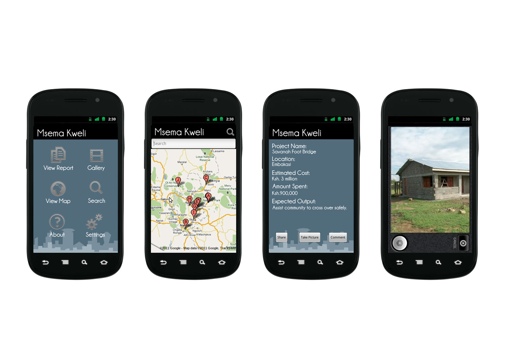
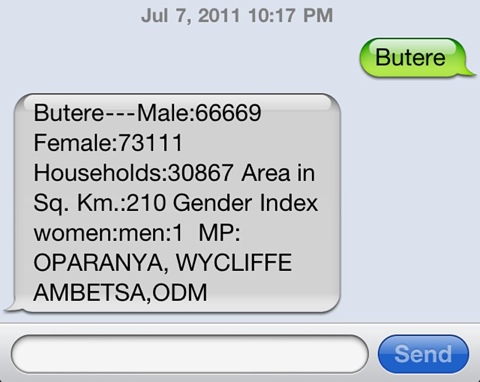
We’ve also created many mobile tools, from an Android-based SMS gateway to customizable iPhone and Android apps.
3 lessons we learned early:
- We didn’t have the credentials. None of us were humanitarians, we just cared about our home and wanted to do something.
- We had no funding. It wasn’t until 4 months later that we formed Ushahidi as an organization, and 4 months after that when we received funding. That didn’t stop us from doing something.
- We had no time. If we had thought long and hard before we built our system, it probably would have been too complicated and wouldn’t have worked. We also might have thought of a more sayable name…
All of the lessons that we’ve learned through our journey are baked into our organizations culture. We question assumptions and we treasure disruption. We’re willing to take risks that leave us open to failure, in our effort to change the way information flows in the world.
There’s a term that I came across last year called “White Space“, and it’s best definition is:
“…where rules are vague, authority is fuzzy, budgets are nonexistent, and strategy is unclear…”
The most innovative ideas come from this white space; internally within organizations, in the startup space and in society in general. At the end of the day, much of the white space definition looks a lot like where I live and work in Africa. And I think it’s why its sometimes easier to come up with innovative solutions there, and why we’re going to see an increasing number of solutions to the problems in the West coming from places that look a lot like Africa.
The best disruptive ideas come from the edge. So, let’s look at the edge, cases from around the globe, for some examples of how technology is being used to make an impact on violence prevention.

- HarassMap (Ushahidi + FrontlineSMS) – Egypt
- BullyMapper (FrontlineSMS + Ushahidi) – Australia
- Human Rights (Ushahidi) – Saudi Arabia by Amnesty Int’l
- YoungAfrica Live (Internet via mobile) – South Africa
- YETAM (FrontlineSMS + Ushahidi) – Benin by Plan
- Apartheid Watch (Ushahidi) – Israel and Palestine
- Hollaback (Phone cameras and a website) – US, India, Mexico and Argentina
- PeaceTXT (SMS and trained people) – US
- Maps4Aid (Ushahidi) – India
- Take Back the Tech (Ushahidi) – Global
“Across the globe—and without any organizing or mobilization by NGOs or watchdogs—people confronted with threats to their rights are communicating out those experiences, in effect reasserting agency over their own rights protection.” – Amnesty International
Those are all exciting examples, showing what can be done with new technology. Suddenly there are no barriers to entry, anyone can take part, and it doesn’t require that someone have authority to begin. It’s just a matter of figuring out what you want to do and galvanizing a community to take part.
Is technology a panacea? Not at all.
As my friend Clay Shirky says, “The technology only becomes interesting when it is no longer interesting to technologists.”
We use a graphic in Ushahidi to remind users of our tools that the technology is only a small part of any solution. We say that 90% of the work is non-tech related, and can take the form of organizing, outreach, branding, translation, etc.
It’s a reminder to us as well, that we need to focus on creating tools that augment human activity and get out of the way as much as possible. That, in the end, is what makes the earlier examples so interesting; they worked because they used the simple tools available in people’s pockets to interact and bring attention to a much larger population, audience or intermediary.
Just this week a new site was launched, like it’s predecessor in Egypt it’s purpose is to draw attention to the harassment that women get, this time in Ramallah, Palestine. Residents of Ramallah, as well as staff from Palestinian women’s organizations and civil society came together and did something, they built Streetwatch. It was self-organized, it emerged from local needs and tools were found that could suit them.
“They have an opportunity to help themselves and other honest citizens of Ramallah to isolate the problem areas and say no to sexual harassment.”
This is the new story of our time, that:
“Our voices revolutionize the world.” – David Kobia, Ushahidi
Those 5 words. That simple statement.
The revolution is here, you’ve watched it shake industries, rock countries and effect your own community – and what you’re seeing is only the beginning of the massive changes sweeping across the world.
It’s not complicated. It’s the effect of technology democratizing information and changing the way it flows in the world.
It’s simple solutions, by unqualified but driven people, like the communities in Ramallah, Egypt, India and even here in the US, that provide a foundation for the changes that we’re seeing. It’s ordinary people, using simple technology to organize themselves and take care of their own problems.
Your task is to look closely, to understand the basics and then figure out how to use these new tools at your disposal to make a difference. In your case, to specifically prevent violence and help those who have been hurt.