I’ve argued before, alongside others, that the main inhibitor of ubiquitous and perpetual internet connectivity at a global level isn’t a technology problem, it’s a business model problem. Mostly the tech exists to put the signal everywhere. What we overlook when we say this is, that while that is true, it’s unsavory to point out that many of “those users” are not valuable – that the population covered won’t make a good return on business investment. So, even if you covered the initial cost of the equipment outlay in those areas with a subsidized government funds, without a proper business model to support the ongoing operations of running the network, then the ROI would be weak and maybe even negative.
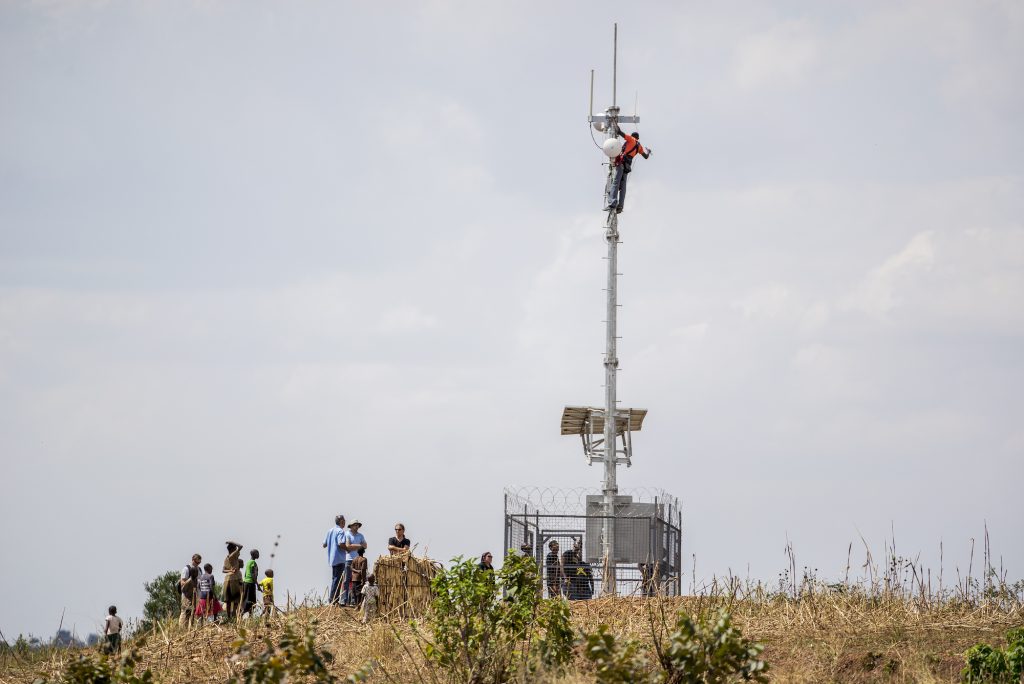
The unspoken technology issue
Many of the incumbent ISPs and mobile operators have sunk too many resources into legacy technology, and then subsequently, outsourced their technical capacity and platform knowledge to foreign firms. This leaves them in an unfavorable position when it comes to new technology that would decrease the cost of rollout by up to 90%, or of taking advantage of how software is changing the way networks work. Due to heavy GSM investment, the industry thinks it best to switch those from 2G/EGDE to 3G. This misses the mark though, it’s iterative change driven by sunk costs, ignoring the fact that we’re moving to a data-only network world. GSM is a dead man walking. IP networks are the future.
It’s not just me saying this, two years ago Deloitte was saying,
“African MNOs should create business models around smartphone users and brace for the rise of the data exclusives and data centric phone users.”
This then provides the opportunity. This is the time to bring new networks without legacy business or technology paradigms, and the ability to apply web-scale economics to the network itself, backstopped by new open software stacks and business models that don’t rely solely on end-user payment.
Fortunately at BRCK we’ve been able to find great investors and strategic partners who see this bigger picture and understand the investments needed to make change happen in this connectivity industry of ours. BRCK, alongside some other firms, are on the forefront of changes happening across all types of data pipes, at the infrastructure level all the way through to the retail side – for both people and things. And as we start running the numbers it becomes increasingly clear just how big of an opportunity this actually represents. It only helps that many incumbents are stuck in aged technology stacks and legacy business models, so the window for positive change is here and profits are substantial.
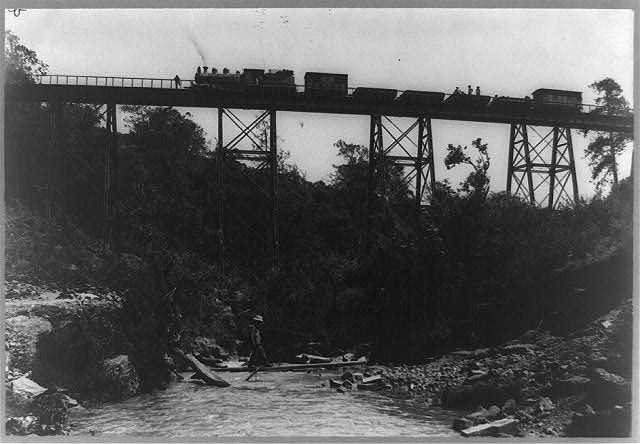
A new railroad
I tend to think of what we do in the connectivity space as similar to our forebears building railroads, making it easier, faster and more efficient to move data and connect far-flung parts of the world. The 1990’s brought us the rebels in the form of scrappy upstart mobile operators and ISPs, they were real cowboys and renegades then! Inspiring leaders, courageously trying everything from pre-paid credit models in Africa, to thinking of mobile credit as cash, to digging the first fibre cables into the hard parts of the continent. Regrettably, these cowboys have handed the reins over to our modern day robber barons, sitting fat and happy on their oligopolies (or monopolies), and making damn sure that no one else has a chance to build something better if they can help it.
I like to think that at BRCK we are building the new connectivity railroads. The tip of the spear for us is unlicensed spectrum, where we take advantage of the ability to roll out public WiFi hotspots without much in the way of regulatory or political hurdles. We layer this with a free consumer business model, so that anyone who can get that signal can connect and take advantage of the whole internet. The underlying economics of the Moja platform are built around the idea of a digital economy. Businesses create engagement tasks that users can complete to earn value within the system. Users then spend their value on faster connectivity, premium content, or additional services. The flow of value into and out of the Moja platform creates the monetary value necessary to profitably run the network.
This is just the BRCK model though, and as I sit on some global boards and in meetings I hear of the others trying their new models as well. New technology stacks, driven primarily by open source software (and some key open source hardware plays), are a big part of the significant decrease in the cost profile (both CapEx and OpEx). But again, the business models… this is where we see the real changes coming and I’m excited to have a front row seat.
As these new railroads are built, by us and others, there lies such great opportunity for economic growth, social development, and business profit.
Sponsor this article: casino cashlib and casino en ligne yggdrasil