Each year the International Telecommunications Union puts out statistics on the state of mobile and internet data around the world. What I’m interested in is their “Information Society Statistical Profiles 2009 – Africa” report, put out just this week. Here are some key takeaways, but you should really go download the full report for yourself.
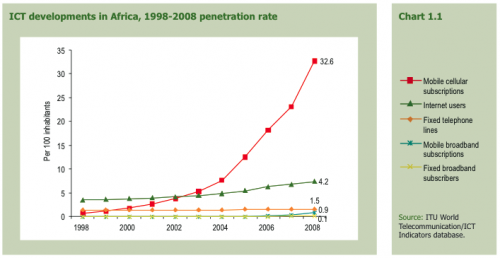
A decade of ICT penetration in Africa
“By the end of 2008, Africa had 246 million mobile subscriptions and mobile penetration has risen from just five per cent in 2003 to well over 30 per cent today. The high ratio of mobile cellular subscriptions to fixed telephone lines and the high mobile cellular growth rate suggest that Africa has taken the lead in the shift from fixed to mobile telephony, a trend that can be observed worldwide. The number of Internet users has also grown faster than in other regions.”
Despite this growth rate, penetration is far below the rest of the world. As the report states, “Less than 5% of Africans use the Internet, and fixed and mobile broadband penetration levels are negligible.” The global average is 23% internet penetration. This is due mainly to cost, but also to coverage over a very large continent that lacks population density outside of major cities.
Not all of Africa is created equal
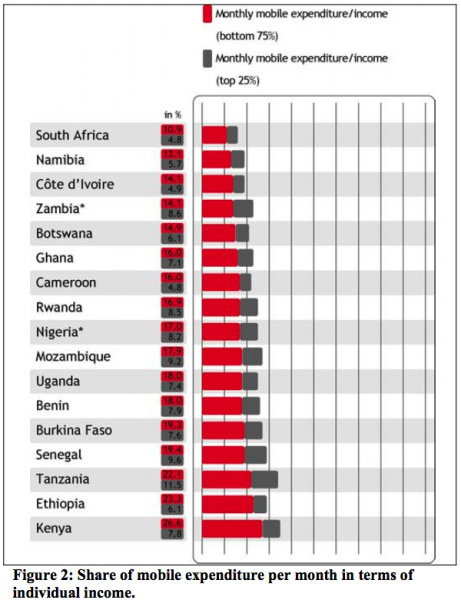
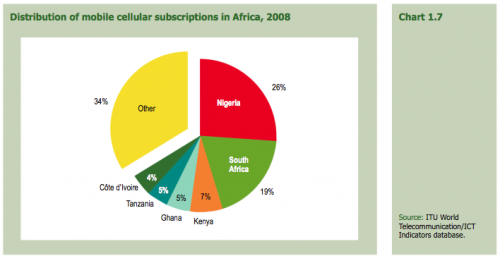
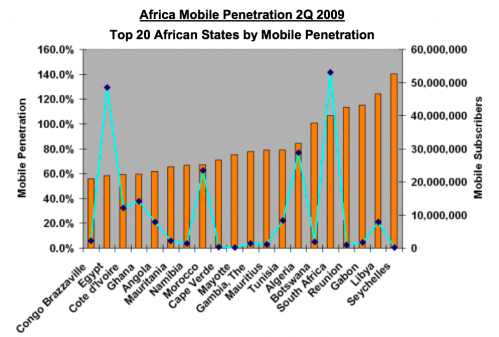
If you’re a company trying to make money off of providing services or products to mobile phone users in Africa, you have to think strategically. You can see from the chart below that the countries you should focus on first are Nigeria, South Africa, Kenya, Ghana, Tanzania and Côte d’Ivoire.
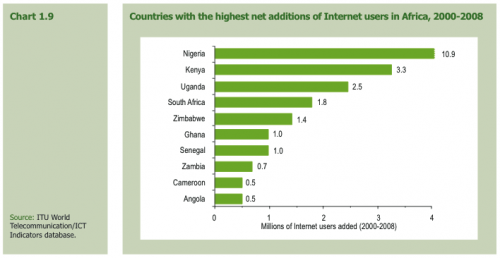
This holds true for the internet as well. You’ll note that many of the top countries for mobile penetration are also countries with a strong internet growth rate.
“According to a recent household survey conducted by Research ICT Africa, the main location of Internet use in such countries as Benin, Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Côte d’Ivoire, Ethiopia, Ghana, Kenya, Nigeria, Rwanda, Senegal, Tanzania and Zambia is the cyber/Internet café.”
Leapfrogging… with a catch
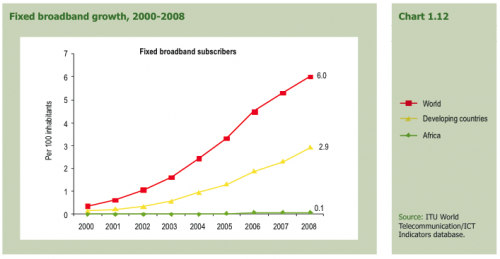
Many reports you read will sing the praises of the mobile networks and how the leapfrogging of landlines has helped Africa. That’s true, and I’m one of those people. However, it comes with a catch, and that catch is that the lack of landlines in Africa means that it’s a lot harder to get fixed-line broadband penetration, whether ADSL or otherwise. This keeps prices high and primarily availability is only in urban areas.
This gives the mobile operators a significant advantage in Africa, and it’s the reason why 3G (mobile broadband) technology is leading the way and why most of the growth will be through the mobile networks.
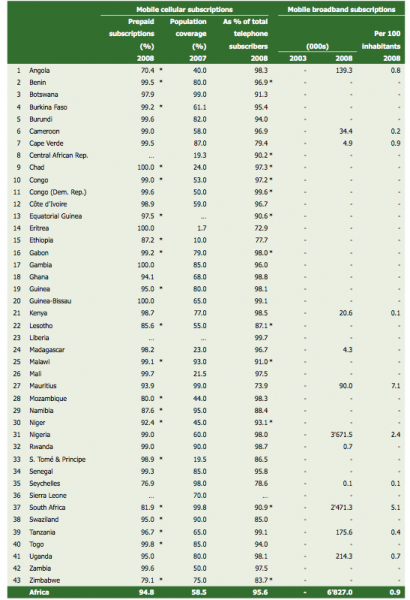
To put it in real numbers. By the end of 2008 there were only 635,000 fixed-line broadband subscribers in all of Africa, representing 0.1% of the population, whereas the world average is 6%. Mobile broadband sees 7 million subscribers with a penetration representing 0.9% of the population, again 6% being the global average.
In Summary
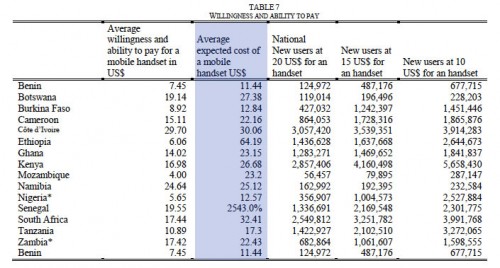
This report is an absolute gold mine of valuable data on internet and mobile phone usage, penetration and growth rates in Africa. I could go on with more graphs and thoughts on each section, but you should do yourself a favor and download the free copy and read it.
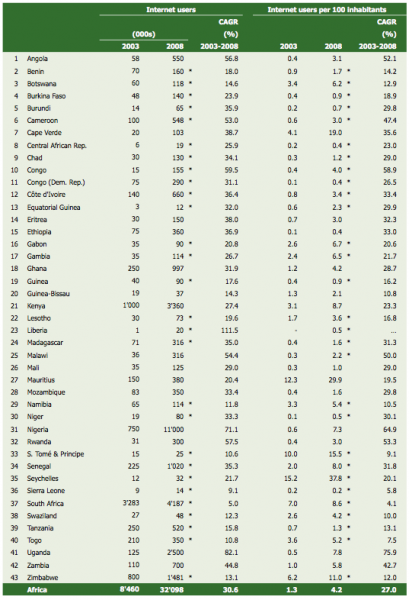
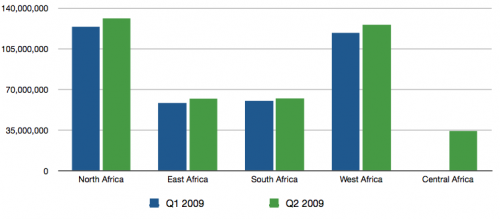
Finally, some last charts showing mobile cellular subscriptions, mobile broadband and internet subscriptions by country in Africa:


 1. Value added services:
1. Value added services: