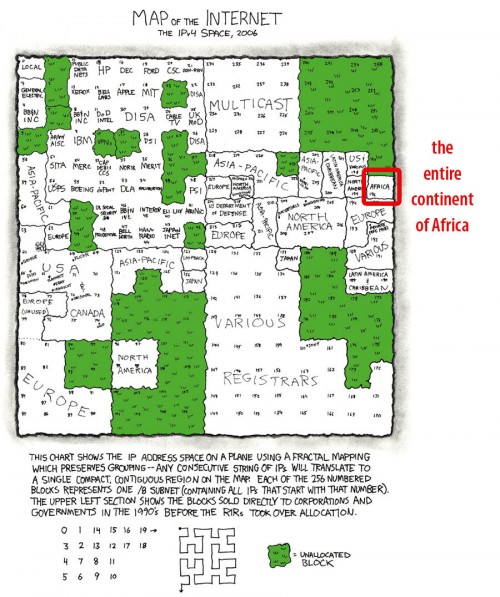
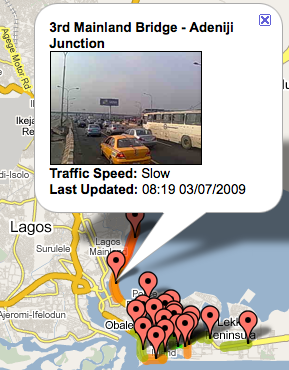
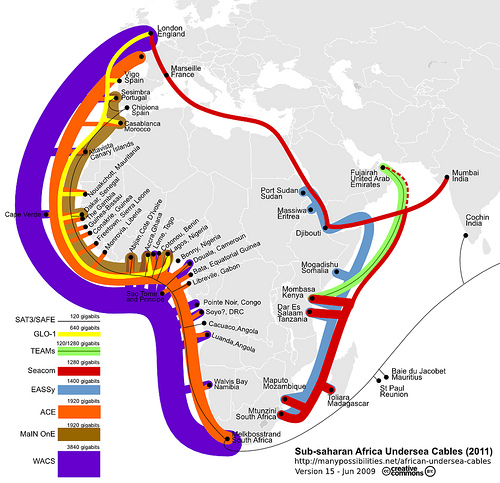
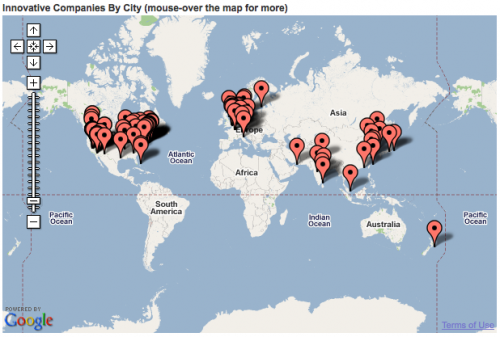
The Map-the-World and Map-Maker teams at Google have been making some major, and much needed, additions for Africa. With a large data push yesterday, Google Maps has one of the most impressive sets of maps on Africa that you can find.
There are now 27 more African countries that now have detailed maps, including:
Benin, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Cameroon, Cape Verde, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Djibouti, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Gabon, Guinea, Gambia, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Madagascar, Malawi, Mauritania, Mozambique, Niger, Nigeria, Reunion, Sierra Leone, Somalia, and Togo.
Comparing countries
What I wanted to do was compare old map tiles with new ones, but I didn’t have any screenshots to do that with. Instead I did a quick comparison of a few countries – those that were just announced vs ones that weren’t on the list.
A good example of this is found when comparing Mali to Burkina Faso in West Africa. There are significantly more town names in Burkina Faso, and all the roads either have names or numbers. In Mali, which hasn’t been done yet, there are some major roads outlined, few towns are named, and no minor roads to speak of.
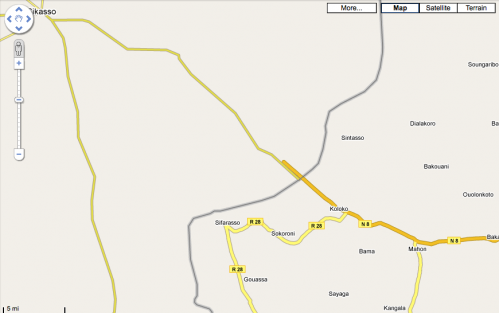
Also of interest, you’ll notice how the roads that should intersect at the borders, do not.
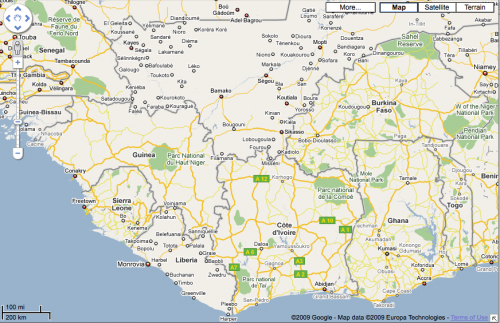
Here’s another interesting view of West Africa. You can clearly see that there has been a lot of data added for all of these countries, except for Liberia and Mali.
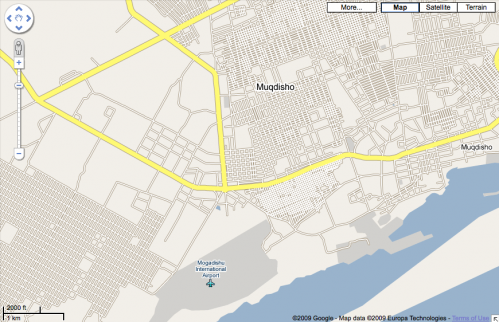
One other interesting map that I came across was of Mogadishu, Somalia. It appears that there either are no street names, or that the Google team working on this didn’t know what they were: