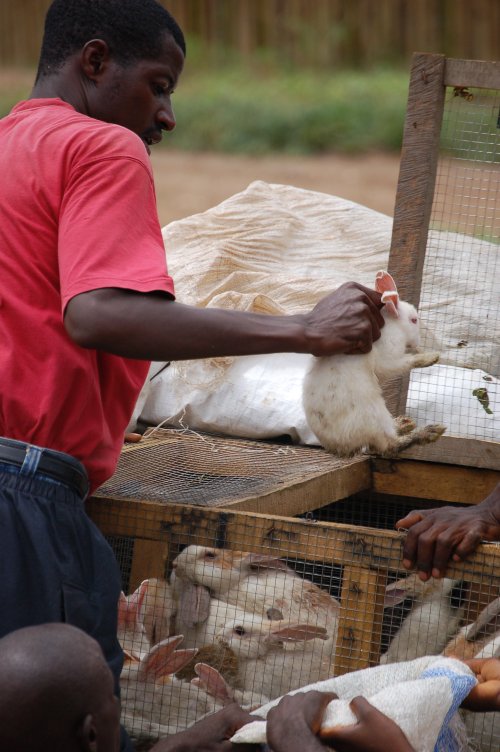
Last year I had a good long conversation with Zach Lutische, a Kenyan with a big idea. It all started with this comment:
“There was a time that I went all the way to Nairobi, only to find out that what I needed was only 1 kilometer away from my farm in Eldoret.”
Zach is soft spoken, but ambitious and energetic. He splits his time between reading the Kenyan tech email lists and time upcountry in his village. He was really excited about putting up a network of rural billboards around Kenya, using them as a way to gather and create a nexus point for community information.
In our day, and being technologists, we sometimes forget that simple and non-digital is still the norm in most of the world. This is especially true in rural Africa. Which is what makes Zach’s concept so intriguing. What he wants to do is marry the worlds of non-technical rural Africa with that of modernized urban Africa.
The Concept
Anyone in the village can put up a notice, news or advertisement on a village billboard by going through a site manager, who would probably be the same person that runs the local mobile phone booth (Simu ya Jamii). Depending upon the size and length of time the notice would be on the billboard, the person would pay between 10/= to 100/= Kenyan Shillings ($.12 to $1.20).
There are a lot of ways these village boards could be used, many outside of what we can think of right now, but here are some ideas for example users:
- Mr. Njuguna has a potato plot and it will harvest approximately 50 bags in August. He runs an advertisement in June on the community billboard and find a buyer in advance.
- A local photographer can advertise and be contacted via the message board.
- City-based companies can go directly farmers and/or sellers in local communities, and be aware of the inventory months in advance.
- Land for sale (with pictures).
- Every village has a market day, the billboard makes it easier for village-based buyers to work with sellers in outlying areas.
A Network of Rural Village Billboards
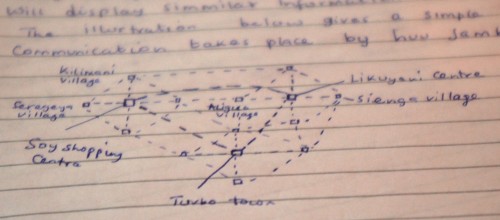
As village billboards start working for the local community, they can branch out to connect to other villages in the area. News and advertisements can then start showing up on billboards beyond a single village, providing more reach to those who are willing to pay.
Zach and I spent some time drawing out and discussing what a pilot program might look like, using his rural community as the testing grounds. We took into account the villages, mapped out their relative locations to each other, their market days and the approximate number of people in each village.
It turns out that each billboard would cost about between $40 and $150 to build, depending upon materials available locally, and on what additions were made – like a small roof to keep rain off of the board.
Augmenting the Rural Billboard with Technology
The above section can stand alone as a business concept. However, where it gets interesting to people like me is in how you take these village billboards and create a powerful melding of the offline and online/mobile worlds that is our present day Africa. This is where the insights and experiences of a rurally raised Kenyan, living in the city and taking part in technology discussions is irreplaceable.
Since the site manager would generally be the person running the local village phone booth, there is the opportunity to sell message space on billboards in other towns, using the mobile information pathways open by these operators. Once you have that network of site managers, you have the beginnings of some very interesting things.
For one, you can now connect these billboard operators locally, regionally and nationally. The ability for end users to both put up advertising and find goods and services is available via digital format or analog. It’s not a big jump to see a nationwide classifieds system growing organically, stitched together by mobile and web services.
Already we see newspapers, like Star, in Kenya taking free classifieds via SMS. What happens when we create a nationwide billboard and mobile phone classifieds network?
Final Thoughts
Africans tend to not be singular. They like to act as a community, so singular actions on mobile phones are less likely than the community coming together around a notice board. So, where mobile phones act as communications between individuals, the notice board serves as communication medium between groups. So, notice boards are the nexus, augmented by the mobile phone.
I think this concept could not only work, but could become something really big. I say that with one caveat. This needs to be done by Kenyans, not some outside entity. The local communities need to be the ones who decide to create and build their own billboards. They need to value it and own it themselves.
The network needs to grow organically from the grassroots up. Not all communities will take to it or support it in the long run, however those that do and find that it makes their lives easier and adds to their lives will pass the word on to other nearby communities, and it will grow. Once a network of community-supported village billboards are up and going, you have the groundwork made for lasting change and a means to build other digitally-connecting services on top of it.