[I probably won’t be able to keep this up all day, but I’ll try to blog/stream what’s happening here at Mobile Web East Africa as best I can. Refresh for updates]
It’s day one of the Mobile Web East Africa conference in Nairobi. This is a new conference, started up in South Africa to great success, and now spreading to other regions of the continent.
Paul Kukubo of the ICT Board
Paul Kukubo, of the Kenya ICT Board, is talking about the future of tech in Kenya, and how the government’s aim is to be a major hub for technology in the region. Explaining how the changes in the industry are brought into context for the government’s vision 2030. He talks about mobile payments, digitizing of government documents and processes, developing software standards and the growing tech community within Nairobi.
Paul continues with mentioning how their approach is to influence policy formulation, intellectual property, data protection, linkages to venture capital and basically catalyzing growth in the ICT sector between government, the public and business.
Rick Joubert of Yonder Media
Rick Joubert, from Yonder Media, “the mobile phone is the most ubiquitous consumer device in the world.” He goes on to talk about how the phone is now even more spread through South Africa than radios. There are 2x as many phones as TV sets. There are 6x more mobile phone subscribers than internet users (in South Africa).
Rick defines the Mobile Web this way:
- Tier 1: The WAP internet
- Tier 2: The mobile web application internet
- Tier 3: Web browsing on phone
**Interruption**
PS Ndemo, who I know and like, is going to give a short address. This isn’t cool, as he’s interrupting Rick Joubert mid-talk (and a very interesting one too). Case-in-point for why government needs to get out of the way more than anything else in the technology field… [Yes, I note that this is probably the American viewpoint on equality coming out].
PS Ndemo is talking through how there were 3.5 million internet users in Kenya last year. Now, with the cost of laptops dropping, we now see 500 laptops sold per day (there were only 20k per year sold before).
Kenya also has the digital villages project (Pasha) with the World Bank is seeing long lines of individuals in far off places coming in to try the internet, get on Skype and figure out how to set up email and other services.
PS Ndemo, ever the gracious person, has at least apologized for the interruption and made amends to the speaker and the conference as a whole. There’s a reason I like him… 🙂
**Back to our scheduled program**
“The Apple iPhone is the number one handset on every continent in the world, except… Africa”. The Nokia 3110 and Samsung E250 are the two biggest phones on the continent. The fact of the matter is, the real money is being made in the inexpensive DVD/Nollywood areas, not in the mobile web yet. Services that play to USSD, Voice and SMS are where the real opportunities lie.
Driving forces:
- Growth in data networks and coverage
- Mobile data access charges
- Local content
- Better quality handsets shipping at the cheapest possible price
- Mobile wallets, mobile commerce, mobile banking
Business models and monetization routes:
- Commerce
- Transactions and financial institutions
- Content
- Advertising
Rick projects that the “size of the prize” in mobile advertising is approximately $8 billion per year in Africa.
Rick finishes showing a video from LynxEffect on how consumers see mobile web, the seductive side of it.

Eric Cantor of AppLab Uganda & Grameen Foundation
I wrote about AppLab and their work with MTN and Google last year. Eric wants to talk about a critical look at a critical space, the 95% of the African population that doesn’t own a smartphone.
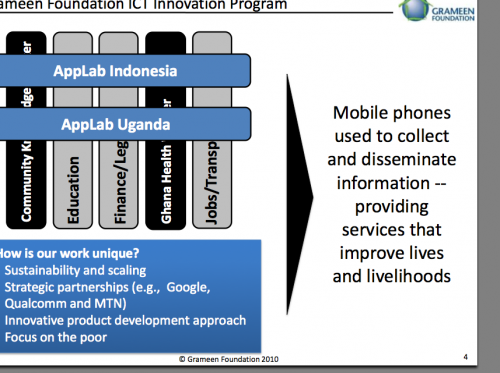
(Get the full presentation of Eric Cantor’s slides as a PDF)
“There are more people having conferences and running too many pilots around the use of social mobile work than there is real practical applications and scaling of the products in the market.”
Technology: Be Patient
SMS is not the only way. It’s very challenging and very expensive to work with SMS. One way to adjust this focus is into voice – people like people, and want to talk with each other.
Handsets need to evolve. Nokia 1100 vs Java 1680 ($20 vs $60) – we’re waiting on the $40 smartphone.
Eric reminds us that we need to get back to the Four-Ps of marketing. We can’t forget user experience, the services might be serious, but still need to be fun to use. At the AppLab they don’t believe what they hear (because everyone says “yes, this product will be great in our market”). They try to dig deeper, learned from Google, on what customers really want and see what people are really using.
Question time
I’ve asked the question for Eric Cantor about why we’re not seeing very simple data hooks built into some of the USSD and SMS applications running in Uganda. (more on this here: “Should we be building SMS or internet services for Africa?“). Eric agrees that there is a lot of upside in that space, and that they’re trying to push more towards the data channel, but until we start seeing more data-enabled handsets in ordinary people’s hands out in the villages, it’s just not a main priority yet.
Robert Alai asks what is driving advertising growth in South Africa? Is it the large companies, or smaller organizations?
Rick responds saying that it’s large companies trying to reach their customers, from banks to Coca Cola and everyone in between. Businesses build grow in this space to find solutions for that, and that’s primarily small innovative companies (like his own), small nimble startups.
Agatha Gikonda of Nokia East Africa talks about the Ovi Store and the opportunities for local developers to create applications and put them on the store to make money.
Peter Arina of Safaricom
What are we going to do to drive interent usage in Kenya? Some stats:
Mobile users are estitmated at 19.05m subscribers. Kenya population estimated at 40m with 22m being the addressable market (15yo or older).
70% of mobile data users spend less than 20ksh on a monthly basis. Industry data enabled handsets estimated at 5m or 26% of GSM users. Cost of a 3G handset is 3x higher than that of a non-data enabled handset. Computer prices are way too high compared to the disposable income of majority of Kenyans.
“The cost of devices that access the internet is the biggest barrier to entry for ordinary Kenyans.”
Cost of broadband (price) is prohibitive due to infrastructure investment.
Local content – the most popular sites accessed on the Safaricom network is Facebook and YouTube. Limited content which is highly priced, is also a barrier locally. There’s a need for high quality data enabled handsets to get good experience.
Conclusion
Mobile data users estimated to reach 10m in the next five years subject to availability of affordable devices, increase awareness, local content development and drop in data prices. Safaricom is trying to work directly with the manufacturers to get more data-enabled devices into normal Kenyan’s hands.
There is a need for more local content that is relevant at affordable rates. Need for reduction in frequency costs, a creation of daily usage habits among users and a need for the government to remove VAT on modems.
Questions
@Kahenya is asking a question. Safaricom is trying to become more affordable, it’s still the most expensive network in Kenya. It’s still has no fixed rate for the mobile data network access. It doesn’t work for small and medium sized business, is Safaricom doing anything to change this?
Peter Arina says they are trying to be cautious. They’re trying to focus on quality (bull$%@& as they have the worst network connectivity in Kenya). He says that they have plans to reduce the cost of data as well, but he has no details on it.
The Safaricom rep says that their main goal is to provide services to the Wananchi (the ordinary/mass Kenyan). The question remains then, why is the cost so high for all of their services?
Paul Kukubo asks when Safaricom will open up their network for value added services for developers and other companies. He’s wondering why the revenue share is so high here (currently if you partner with Safaricom, they’ll take about 60% of revenues), meanwhile elsewhere in the world, like Japan, give 70% to the developer.
Paul asks about the issue with the networks taking advantage of the developers who are out there who come to them with ideas and new products.
The Safaricom rep states that this is not the case any longer. They partner with MobilePlanet and Cellulant (as examples, but it’s a poor one because they’re established companies now). He says that at first they start off with a big chunk of the revenues, but as the product does better, then the developer will get more of the share.
Basically, we get no straight answers from Safaricom and only promises of better things in the future with no details.
Jose Henriques, Executive Head: Online Product Management, Vodacom South Africa
6.65% of the African population currently uses PC internet. The top ten countries make up 85% of that.
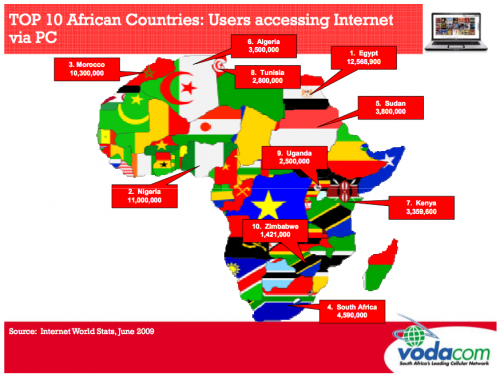
Some more stats:
- Africa represents 15% of the world population, but only 3.9″% of the world’s PC internet usage.
- Africa’s PC Internet users have increased by 1359% from 2000 to 2009.
- The global service revenue generated from subscriptions to mobile internet access are forecasted by Informa Telecoms & Media to rise from $57 billion in 2008 to $120 billion in 2013.
- Mobile ad revenue is estimated to be at $2 billion by 2014. Total value of marketing spend on mobile to be around $6 billion.
- Mobile subscription rose from 54 million to almost 350 million between 2003 and 2008.
- On average there are 60% mobile penetration in the world. In developing countries the figure stands at 48% , which is 8x bigger than in 2000.
- Lack of fixed-line access will drive huge mobile internet usage and revenues.
- Vodacom generates 49 million ad impressions per month in South Africa (big opportunity).
(Full presentation by Jose Henriques from Vodacom South Africa)
Questions
What has been defined as a smartphone, is not what we define one as today. How would you define it?
Cheapest data enabled devices are about 2000Ksh in Kenya. Safaricom thinks that these are smartphones.
Mpesa… Why is Safaricom unable to cooperate with and provide third-party access (opening their APIs) to developers in Kenya for Mpesa?
The Safaricom rep says that they are willing to do this, and that they’re hungry for people to come in with ideas and products. No specifics given on this. @TMSruge, the moderator, asks her to provide details on how they are actively trying to seek out and help grow this as there is no API or SDK.
@wanjiku says she’s heard Safaricom saying that they have a tendency to do well with big companies, but holding smaller company money for 3-4 months, hurting their cash flow.
Steve Vosloo asks what types of local content are people really willing to pay for?
The Safaricom rep is out of touch… she states that, “no one is willing to pay anything for mobile content”. This is bunk.
Rick Joubert comes in to state facts on how much money there is being made in South Africa in mobile content, $540 million is the real number just in SA. It’s not whether people will pay or not, it’s whether they find value in local content.
A question was asked of Safaricom, why they don’t open up the ability for third-party service providers to bill consumers? The answer by Safaricom is that they are. (I can’t confirm this)
We have Zap, Mobile Pay, Mpesa, etc… when are we going to have an agnostic system to send/receive money? by @kahenya
MTN rep says to come to Uganda to see this working. It’s there working on the MTN system. It’s a serious issue of not having your payment system to go beyond your own network.
Mpesa is a wall gardened. Kahenya and Teddy Ruge ask when there will be a need to NOT walk around with 3 handsets to send money within each one.
Safaricom states that they can already do this within their system. They lay the blame at the regulators feet for why it hasn’t happened.
**Lunch**
Brett StClair of AdMob
Brett starts by asking, “what is mobile internet?” It’s a website that is built for mobile handsets. Admob puts banner advertisement on these sites. They server 12-14 billion advertisements into this network each month. The man on the street can earn revenues start advertising today. There’s a 60% payout to publishers.
Have access to 53 countries in Africa. Monthly ads serves is 750 million in Africa alone.
African Mobile Web currently has South Africa, Nigeria, Libya, Egypt and Kenya as the top 5. Data prices do have a huge effect on the advertising revenues available in Africa.
Nokia 3110c is the most pervasive phone in the market (3.8%), Samsung E250 is at 3.7% penetration. Top smartphones are the Nokia N70 at 10.8% and then Nokia 6300 at 10.3% and then the iPhone at 8.2%.
Top reasons why South Africa is working:
- 5 million fixed line internet vs 10 million mobile internet users
- Strong operator billing infrastructure
- However, mobile money is not mature yet
- Early adoption by premium traditional publishers
- consumers traditionally have had a fast adoption rate
- Due to vast competition for impressions average CPC pricing grew from $0.03 to $0.27 in a year.
Is Africa next? The rest of the world thinks it is, but we need to get the local people to understand this.
Cheapest inventory in the world is in Africa… global accesss average is $0.03, in Africa it’s at $0.01. Local contet providers will benefit as they understand the local African consumers.
Key to making this work:
- 3g network coverage
- Cheap data pricing
- GPRS enabled handset penetration
What are the opportunities in Africa?
Strong tend to follow the West and South Africa. Paid for content, reliant on operator billing. Free content, which is ad funded. The top publisher types are communities, portals and downloads. The top categories are music, religion (15%), games and brands.
African traffic is made of 54% Nokia handsets, then 18% Samsung handsets. iPhone requests make up 18 million impressions in Africa.









 It’s not that often that one of Africa’s new web companies makes a big international splash.
It’s not that often that one of Africa’s new web companies makes a big international splash. 
 I entered into the
I entered into the