It’s all beginning to come together, at least on the fringe where all of us technocrats live. Social networks have been humming along quite nicely, many people you know are now part of a service like Facebook, MySpace, Twitter, Bebo or Mxit. On the edges, some applications have started to pair up location-based services around them, thus the rise of smaller applications like FireEagle, Loopt and Brightkite.
What’s always seemed to be missing is a way for location, mobile phones and social networks to coalesce. A way for you to communicate with people, be it updates, comments or chat – and then apply location to that as you chose. Those social networks that tried to do it all couldn’t do it at this level, because they didn’t have critical mass (such as Brightkite). Those that had reach, like Twitter or Facebook, don’t have a simple way to play with location for everyone.
Enter Google Latitude
Just over a week ago, Google Latitude launched. It’s a location-based service that mashes up Google’s own mapping products with Google’s communication products; Gmail and gTalk (chat). One week later, they announced that a million people were already using the service in the 27 countries that they had released it into.
While people are discussing how great the technology works, and it does seem to be quite impressive if you carry one of the supported smart phones platforms (BlackBerry, Windows Mobile, Symbian and Android), I believe there’s something even bigger going on here. Google has not had much success in the social network space, so they are taking a rather nontraditional approach to getting embedded into people’s lives at a much more foundational level. Gmail has a base of 50 million+ accounts, and each comes with a chat service, which has gained quite a bit of popularity. Not to mention, SMS was enabled within chat just a couple months ago, in December.
What Google appears to be doing, is leveraging its massive user base, tied together through email and chat services, and pairing it together into a larger community that works within it’s mapping infrastructure.
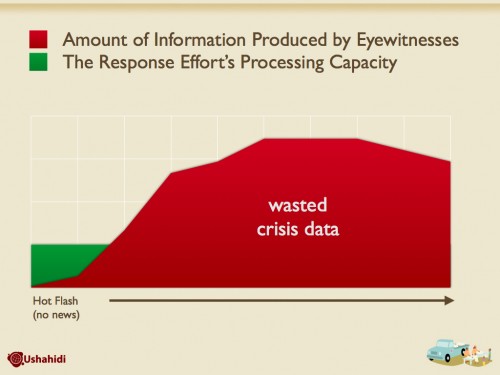
(Putting on my Ushahidi hat, this has some pretty big ramifications for disaster and emergency work in locations where Google use is heavy.)
The competition
It also has the potential to change the game for some other large services. What happens if people start using Google Latitude for their status updates instead of Twitter and Facebook? What service do you use to find out what’s happening on a Friday night?
It will be very interesting to see what types of reactions to this service arise out of the large social networks, especially those with a large international footprint. Getting location, mobile and social networks to play together isn’t easy, yet these organizations will not sit by as Google whittles away at their empire.
Here’s something to think about. If you didn’t realize this before, pay attention: the big international showdown in this space is between Google and Nokia in the coming years. They have been gaming each other for over two years, and as the race to the edges begins, you’ll see them come head-to-head more often.

1.5 years ago Nokia bought mapping service Navteq in a mega-deal at over $8 billion. Last summer they launched Ovi, which allows remote sync capability for photos, contacts and calender, gains access to music and games, and marries up their mapping and sharing capabilities. It’s what Nokia is banking on for their consumer value-added services in the future.
I’m not sure who will win out on usage in the end, but I do think that Google’s Latitude is an incredibly strong and under-the-radar type play that should be watched very closely. One thing is for sure though, the organization that opens up for easy third-party development on their platform will have a better chance.