(Note: cathartic, bloated essay forthcoming, read at your peril)
Say you are a Kenyan web designer living in Seattle, do you think anyone cares that you came from Kenya? No, they only care that you are a great web designer.
If you’re an American programmer working in Nairobi, does anyone care that you come from the US? Yes, for some reason that matters. You’re judged on where you come from as well as your skill set.
It’s not apples-to-apples, though it should be.
This is at the heart of an issue that I’ve seen played out many times over the years in Kenya. My position in the community, my background in Kenya and the US, and the organizations I’ve built locally give me a unique perspective on what’s going on here culturally, that sometimes is hard for others to see.
Americans, Europeans, etc want to work in Kenya and be part of a growing melting pot of engineers, web designer and entrepreneurs trying to build out the next great tech economy. It’s a grand dream, and one that we should all support if we want Kenya to be on the global map.
Kenyans are madly building companies, growing a new breed of programmers, designers and entrepreneurs that are waking up to the reality of a global market. It embodies all of the energetic vibrancy that makes Kenya a regional economic powerhouse.
Both are needed. However, all things are not created equal, which leads to tension.
Kenyan tech has global competition, so act like it
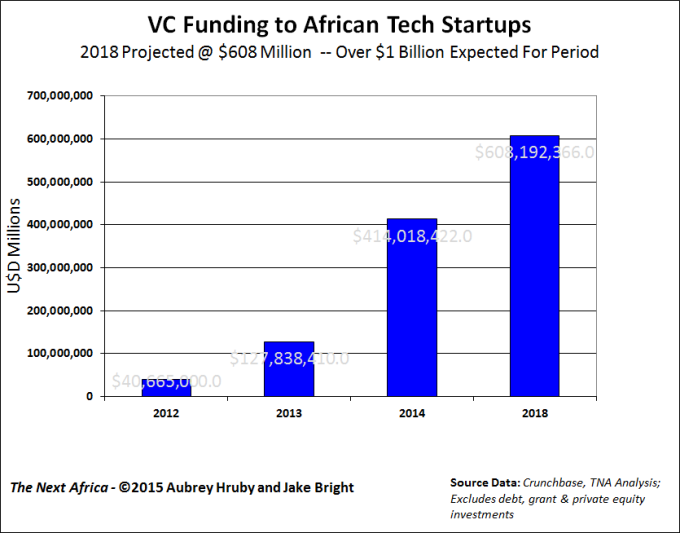
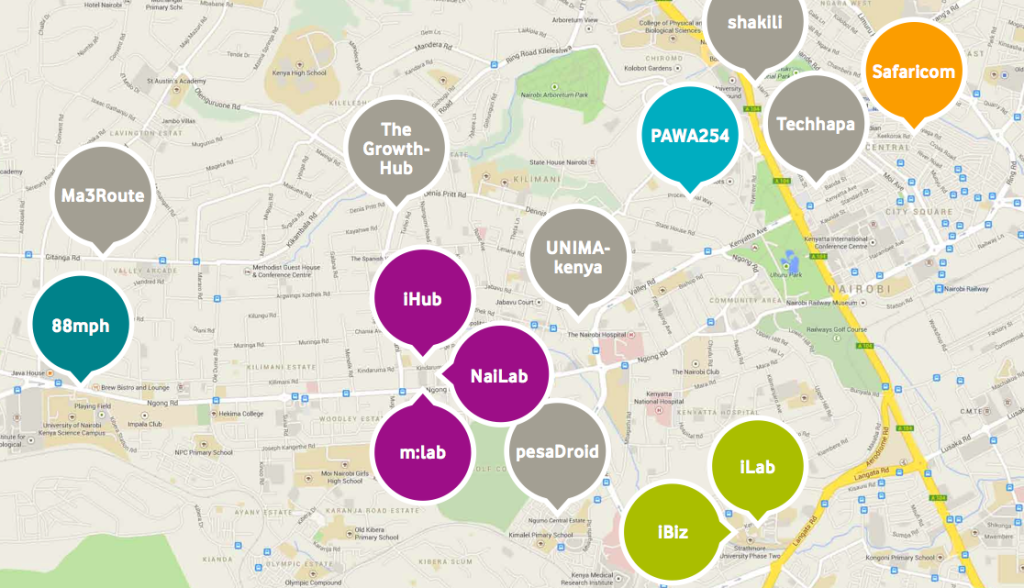
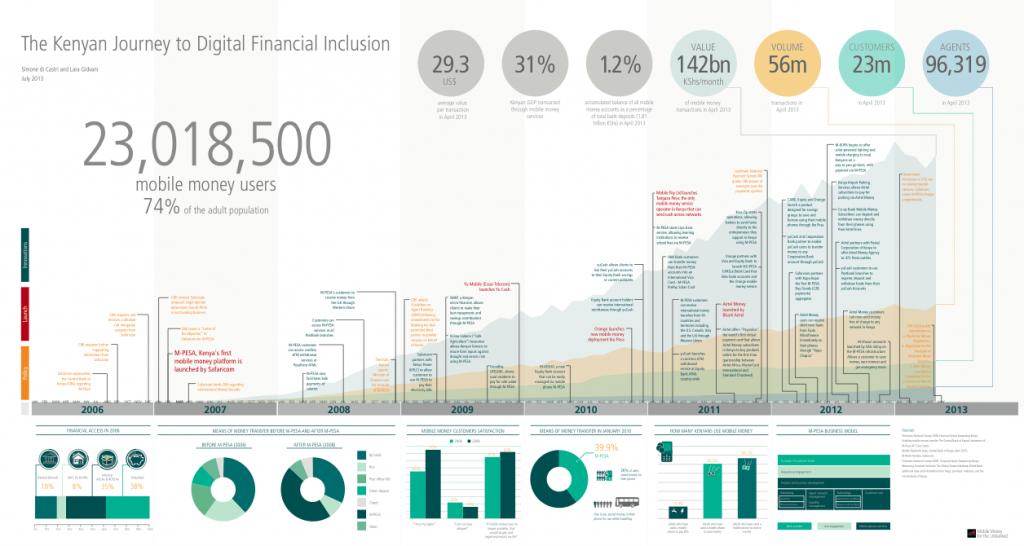
I often talk about the Kenyan tech scene as highly active, yet nascent. There is a great deal happening in our space, but it’s not nearly as big as other larger and older tech communities found in the Bay Area, London, Berlin, Israel, Moscow, Bangalore or New York City. We’re growing, we’re half-way up the mountain, and there’s still some climbing to do.
There is likely the same percentage of top level engineers and designers in Nairobi as anywhere else, but the pool is still small. I’d guess the total pool of engineers is somewhere in the 3,000-5,000 range, and designers are only about 100-200. It’s not a deep pool to pick from, and there are many who linger around the edges claiming that they have skills, but who aren’t qualified to do more than create a “hello world” website.
In the startup world, Kenyan-led companies tend to be under-resourced and without the same networks that make it so much easier for expats to get started. While we’ve been building up more and more base resources locally for seed capital, and the business acumen of the founders is improving due to them being in town, it’s still not enough. And, while the $25k accelerator level is very much present in the community, there’s a huge gap in the $100-500k investment levels.
So, with local entrepreneurs, this leads to a protectionist mentality about how many mzungu’s are around and how they are sucking up resources. It’s not a good place to be. What we need to realize locally is that in the tech world there are very few borders, that we’re automatically in a global playing field. There needs to be lighter rules for immigration of expats (from anywhere) who are willing to bring investment and talent into the country, and keep it here.
If anything, Kenyan lawmakers should be finding ways to reduce the ludicrous tax rates on software companies, which would incentivize local ownership, encourage local investment so that the companies that do well have their profits stay in-country, and try to attract international talent and grow local talent. It’s a long-term game, and will pay off in the years ahead.
US/EU immigrants need to understand where they are
On the other side of the fence are the international expats who enter into Kenya. They are often well-meaning folks with a desire to build a company, or be part of a company in this vibrant country brimming with opportunity. This should be encouraged.
What I’ve observed over the years however, is something that shouldn’t be encouraged. These immigrants who come into Kenya tend to hang out with each other. This isn’t strange at all, Kenyans tend to do the same when they’re in the US. What’s not healthy is when you spend most of the time around people who look and sound like you, then when you want something from the rest of the greater community, act like it’s not there because it’s not directly in front of you.
There are some amazing programmers in Kenya, some ridiculously good web designers, some top-notch entrepreneurs. You will not find them by throwing a dart in a room and hoping to hit one.
Complain all you like about immigration policy, the need for more high-level talent being brought into the country, business taxes, etc – and I’ll be right with you. You complain about there not being any local high-level talent and I’ll call BS.
Instead, get out and get to know people. Get outside of your expat bubble and be a part of the community. This isn’t just meetups, this is who you go grab a drink with, who’s wedding and hospitalization you attend, who you watch rugby with and who you help (and are helped by) when in a bind. This is Kenya, where relationships matter, and where they are earned over time. Friendships here aren’t given lightly, and when they’re given, then they mean something.
To many in Kenya, the expats come and go, so why should they be invested in? Sure, make “friends”, and see what can come out of it, but the problem is that we all know the expat will be gone in 2 or 4 years. The deep investment we expect out of our relationships in Kenya isn’t found in that kind of transient immigrant mentality.
A personal final recap
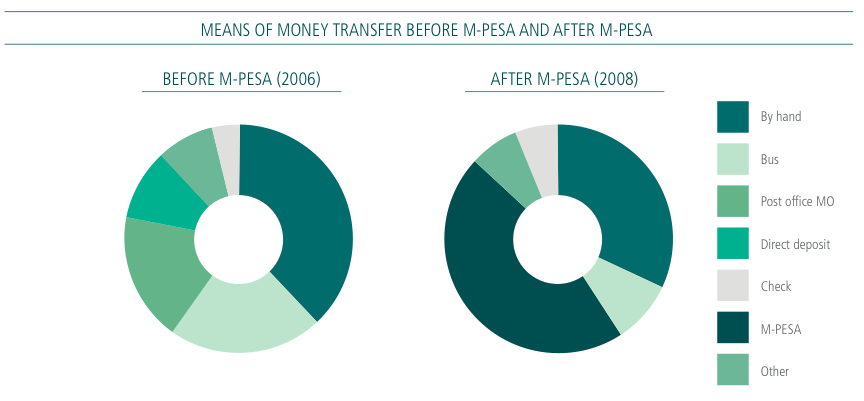
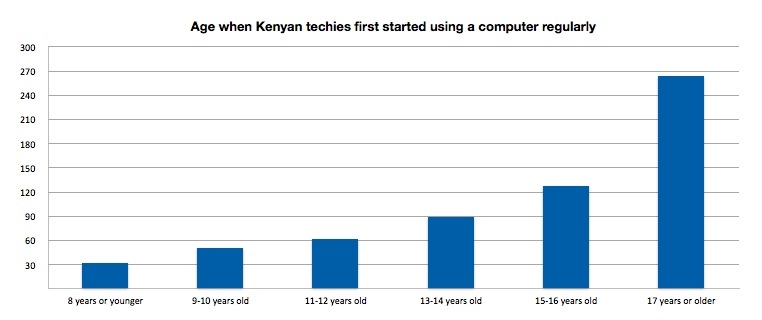
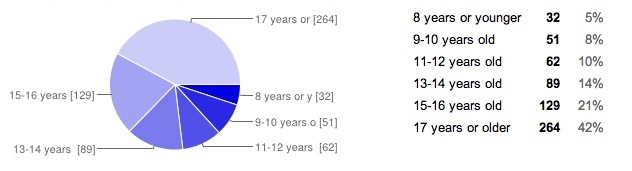
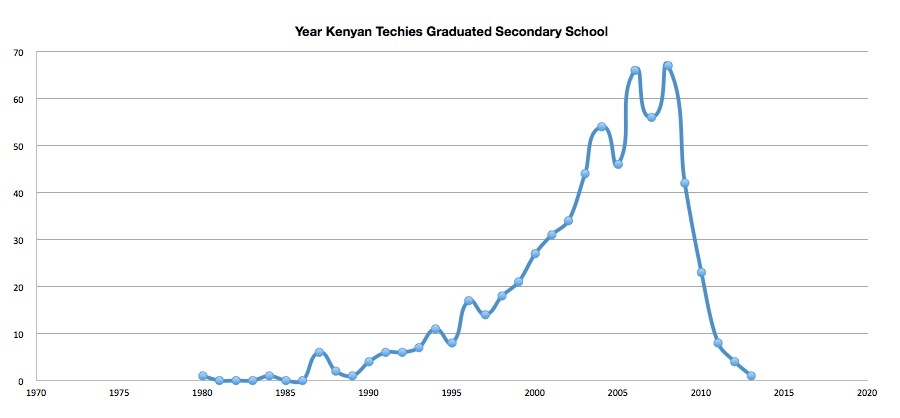
Back to the talent issue. I’ve had the honor to work with some amazing Kenyan programmers, designers and engineers. How was I able to find them? It turns out that the relationships that I started building back in 2006 (8 years ago), then continued throughout the years, opened my world up to the people who really know what they’re doing. I courted some for 3+ years before they finally joined my team(s), others that I’d like to join my team still won’t budge from their old positions.
Right now I’m looking high and low for an electrical engineer for BRCK, senior-level EEs who have telcoms and/or consumer electronics backgrounds aren’t in deep supply in Kenya. However, I know they’re here, I just have to look harder and keep pushing out beyond my normal network.
They’re here. They’re not easy to find and they might already have a great job. Your lack of being able to find them doesn’t mean they’re not here. Your inability to attract them to your organization isn’t their problem, it’s yours.