As with most CEOs of younger companies, I find myself on the investment raising treadmill. Doing so for a company focused on internet connectivity in frontier markets provides an extra layer of complexity, since it’s not a sexy of a proposition as a new app for ecommerce, agtech, fintech, etc might be. Those are easier to invest in since you’re playing with a world of software, not any hardware or infrastructure to muddy your hands with. Unfortunately, in my BRCK world, we have to deal with atoms, not just bits and bytes (though we do those too). Which is why many of my conversations find me explaining why connectivity is critical – thus this post.
What I find interesting is that everyone wants to benefit from a basic underlying availability of connectivity, but few understand what it is or why it is so important. If you’re with me at a public event, I’ll eventually spout off something along the lines of, “you can’t have a 21st century economy without power and connectivity.” This is my simplified way of stating that for any industry to be meaningful on the world stage (or even their own country stage), they need the ability to move data. If power and connectivity are the foundation, then the aforementioned ecommerce, agtech, fintech, and others are all pillars that stand on that foundation.
Economic growth
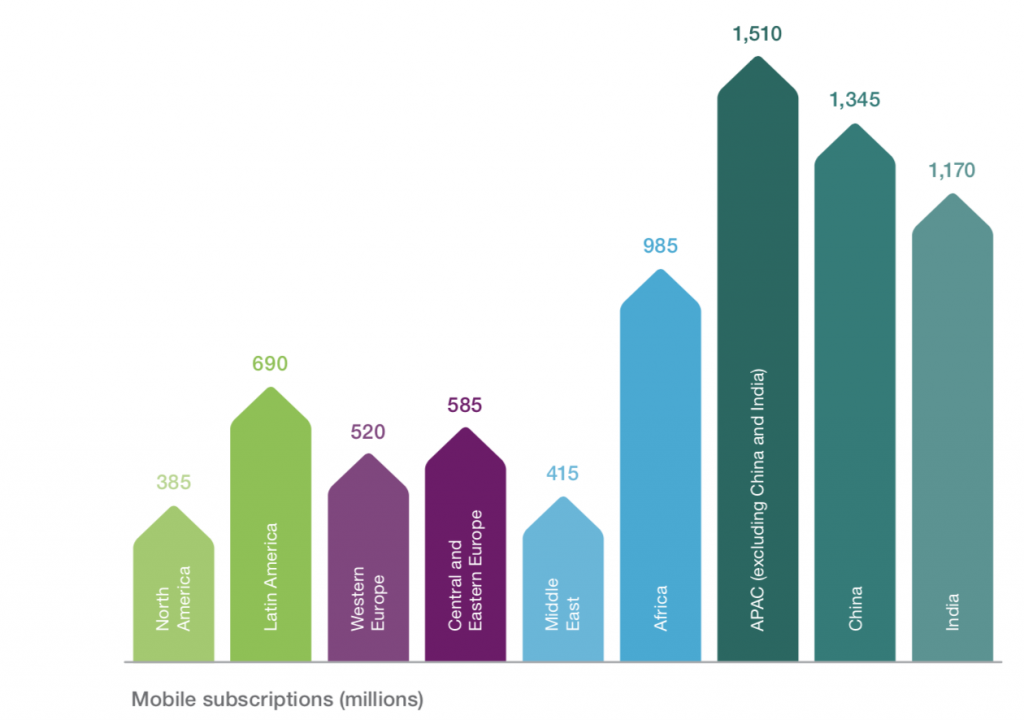
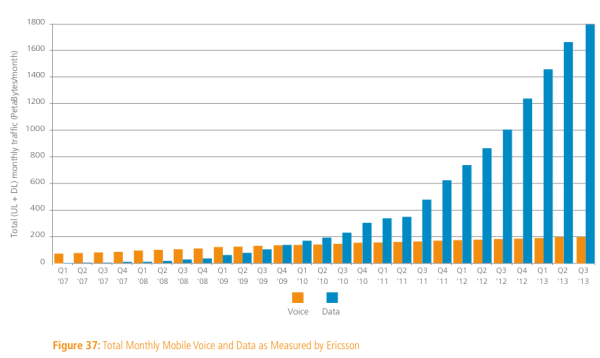
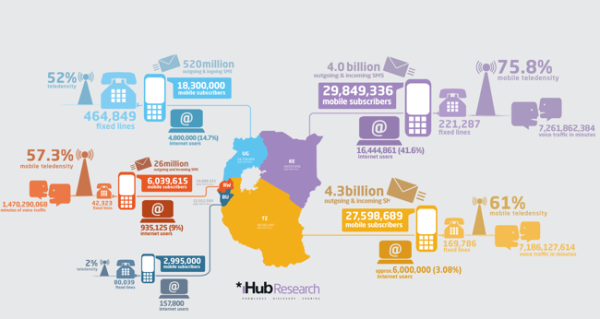
I’ve written before on how smartphone penetration has reached critical mass and proceeds on a noteworthy trajectory across Africa and other frontier markets. Africa, coming from a largely 2g/Edge based on old legacy GSM technology will have some of the highest growth rates in mobile data subscriptions globally, driven by chat apps and mobile video, as we transition to data-only networks. In 2022, there will be eleven times more mobile data traffic in Central and Eastern Europe and Middle East and Africa (Ericsson 2017).
- 250M smartphone subscribers in 2016
- 770M by 2022 (Y-o-Y growth of 30%) (Ericsson 2017)
- Over half of mobile phone shipments into Africa in 2016 were smartphones (Deloitte 2017)
All of this means that there are millions of new customers available for new, smart, and data-intensive financial products, agricultural services, marketplaces, logistics, and the list goes on. This is why we’re seeing the rise and rise of startups in these spaces, as well there should be.
What we’re not paying attention to is this: the market is still smaller than it could be.
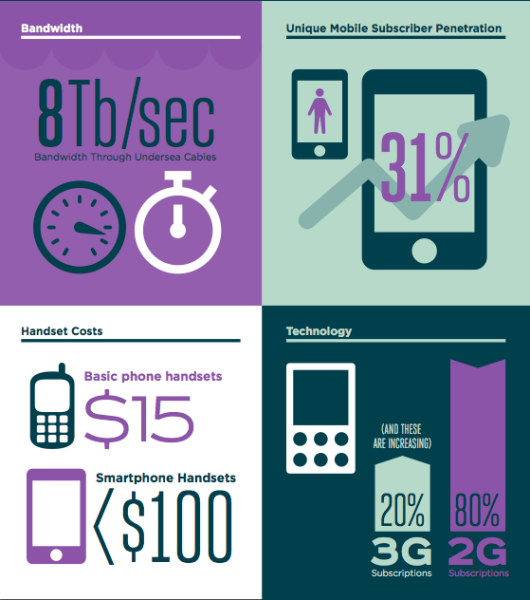
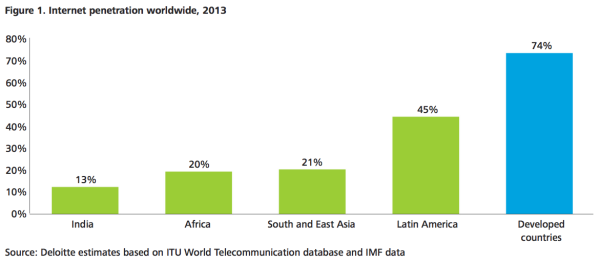
Imagine that you’re finding amazing market traction with your new mobile lending app, or with your logistics system, or with your online goods marketplace. Imagine that you’re doing well, however did you know that you’re only reaching 20% of the people who own smartphones in the country…. Oh, right, that’s the piece that’s surprising! You could be doing even more, growing faster and capturing more market share if only the other 80% of smartphone owners in your market could afford the costs of getting online regularly to use your service.
This is where BRCK is stepping in with our Moja platform (free to consumer internet). You’ll benefit greatly from our growth. We’ll benefit greatly from your growth.
Social development
Even though I’m largely driven by the economic reasoning for connectivity alone, since I believe that the best way for us to make significant change in Africa is to grow wealth for everyday Africans, there is a strong social argument for widespread and affordable connectivity as well.
Connecting an additional 2.5 billion people to the internet would add 2 trillion dollars per year to global GDP and create 140 million jobs
- It enables improvements in health (Deloitte 2014)
- Unlocks universal education (Deloitte 2014)
- Strengthens civil society through public services, social cohesion, and digital inclusion (Deloitte 2014)
It turns out that if we connect people to the largest, greatest network of knowledge and information in the the world, then a lot of great social benefits are realized across a number of important areas. It’s hard to argue against more jobs, better education, better healthcare, more informed citizens, and a stronger civil society in any country.
Connectivity is the foundation
Like everyone else not involved in the plumbing and distribution of the internet, I used to think of this only academically. It’s easy enough to understand and think through intellectually. However, I found that in living it, in dealing with the practicalities of the internet, in coming to know the end-user I began to appreciate just how important connectivity is. Building a new app or service can have big effects, changing the affordability equation for connectivity and you send a shockwave reaching everyone, everywhere.
Sponsor this article: best iphone casinos in canada and grand mondial casino