[This is a guest post by Ben Lyon of Kopo Kopo, and recently of FrontlineSMS:Credit, who I consider to be one of the leading experts on mobile money, banking and payments in Africa. Kopo Kopo aims to make the integration of microfinance and mobile money as affordable as possible by offering a software-as-a-service that connects m-money transaction data to customer accounts in a range of common loan management systems. You can follow Kopo Kopo on Facebook and Twitter.]

Kenya is by far the most exciting, innovative mobile money market on earth. Below is an overview of some of the major and upcoming players.
MAJOR PLAYERS
Safaricom M-Pesa
Launched in March 2007, Safaricom M-Pesa was the first mobile money system in Kenya. It is now the most successful mobile money deployment on earth, boasting use by 51% of the adult population. In addition to person-to-person transfers, you can use M-Pesa to remit funds from the UK to Kenya, pay bills, purchase goods, buy airtime, and, with the launch of M-Kesho, move funds to and from an interest-bearing account with Equity Bank. Fun fact: Safaricom M-Pesa has more agents in Kenya than Wells Fargo and Wachovia have ATMs in the United States.
Airtel Money
Formerly Zain Zap, Airtel Money is the second largest mobile money system in Kenya. Prior to its acquisition, Zain was focused on creating a “cashless society†whereby any number of needs could be met via mobile money. Zain was also committed to its notion of One World, the idea that a Zain customer in Country X should be able to call a Zain customer in Country Y a at local rate. One World was the source of much speculation with regard to international person-to-person mobile money transfer. It will be interesting to see if / how Airtel changes course, especially with regard to pricing.
Orange Money
Orange Money launched in late 2010 in association with Equity Bank. Instead of offering the same features as M-Pesa, Zap, or yuCash, Orange opted to create a de facto front-end for Equity Bank accounts, allowing it to exceed regular transaction and m-wallet balance thresholds.
Essar yuCash
Essar yuCash launched in December 2009 and is powered by Obopay. yuCash offers some standard features such as person-to-person transfer and balance inquiry as well as some unique features like requesting money, adding a short message to a payment, and inviting friends to join. yuCash is also unique insofar as it offers five different front-ends: WAP, SMS, Voice, USSD, and STK.
Equity Bank
Equity Bank is the largest microfinance institution in Kenya and is nothing short of a powerhouse. It has an extensive ATM network throughout Kenya and has integrated with M-Pesa (M-Kesho), Orange Money, and yuCash.
Musoni
Musoni is at the cutting edge of microfinance, enabling loan disbursal and repayment via Safaricom M-Pesa and Airtel Money. Musoni plans to conduct country studies in Rwanda, Tanzania, and Uganda in the coming years.
Paynet Group
Paynet is responsible for all Visa transactions in Kenya, interchange for 2,000+ ATMs, and PesaPoint. Due to their interaction with Visa, they are PCI DSS compliant, meaning that their system is both redundant and incredibly secure. Paynet aggregates and formats transaction data for several mobile money providers in East Africa.
UPCOMING PLAYERS
iPay
A product of Intrepid Data Systems, iPay enables merchants to accept online payment via Safaricom M-Pesa, Zain Zap, and Essar yuCash. Prominent users include PewaHewa, Fenesi, and Zetu.
PesaPal
PesaPal is a product of Verviant Consulting that, according to CEO Agosta Liko, aims to “make sense of the Kenyan payment landscapeâ€. PesaPal lets online merchants collect payments via M-Pesa, Zap, Google Checkout, and a range of common credit cards. Their latest product, e-Ticketing, allows event organizers to accept online payments for registration via mobile money.
M-Payer
A recent product of Zege Technolgies, M-Payer enables real-time mobile money transaction processing. The CEO of Zege Technologies, Kariuki, played an instrumental role in the M-Pesa / Equity Bank integration that resulted in M-Kesho.
Lipuka
Powered by Cellulant, a company that serves 60M+ subscribers throughout Sub-Saharan Africa, Lipuka integrates bank and payment channels to enable music downloads, bill payments, and information services via WAP.
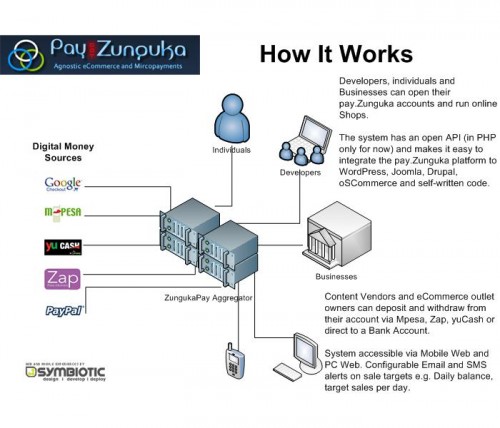
Moca
Formerly called ZungukaPay, Moca is a product of Symbiotic Media Corsortium. ZungukaPay enabled online merchants to accept payments via M-Pesa, Zap, yuCash, PayPal, Google Checkout, and a range of common credit / debit cards. ZungukaPay also had an open API for integration purposes. The new product, Moca, takes a different turn by enabling customers to buy ‘Moca credits’ via mobile money, which they then use to pay for goods and services on partner websites (e.g. KeleleMobile). Fun fact: selling non-refundable credits precludes Moca from being seen as an e-money issuer by the Central Bank of Kenya.
JamboPay
A product of Web Tribe Limited, JamboPay is an “Online Checkout & Micro-Payment Service†that enables merchants to accept online payments via M-Pesa, Zap, yuCash, and Visa credit/debit cards. JamboPay has a tariff structure similar to PayPal in the US: a commission per transaction + a flat fee for any transactions initiated over the JamboPay web platform.
MobiKash
MobiKash, a third party mobile money provider, is operated by MobiCom Africa Limited in partnership with Sybase 365 and Seal Systems. MobiKash leverages USSD to give Kenyans on any mobile network real-time access to accounts at participating banks, including Post Bank, National Bank of Kenya, and Trans National Bank. MobiKash uses the Sybase 365 Mobiliser Platform.
KrossPAY
Formerly PesaPot Holdings Limited, KrossPAY worked with PAYG Solutions to develop a hosted core banking and financial management platform for microfinance institutions, credit unions, and community benefit organizations. Some PAYG Solutions programmers were involved with the creation of M-Pesa, so there may be a mobile money integration in the works. KrossPAY also offers a “universal mobile money transfer and payment†service called CaribPay.
Jipange KuSave
Jipange KuSave is an initiative of Mobile Ventures Kenya Ltd., a subsidiary of Signal Point Partners. Launched as a pilot in 2010 in partnership with FSD Kenya and CGAP, Jipange KuSave aims to extend affordable micro-savings and micro-credit to the ‘mwanachi’ (Kiswahili for ‘common man’) via mobile phones.
Tangaza Limited
Managed by Mobile Pay Limited and a network of independent trustees, Tangaza enables both local and international money transfer as well as services like utility bill payment and remote airtime purchase. Tangaza is accessible via USSD and the internet and works across multiple mobile networks.
NOTABLE M-MONEY INTEGRATIONS
PewaHewa
PewaHewa is similar to the iTunes Store insofar as you can browse for musical artists, albums, genres, etc. and purchase songs via mobile money. PewaHewa is powered by iPay.
Kalahari
Often referred to as “the Amazon.com of Africaâ€, Kalahari offers a wide range of online goods and services, which customers can pay for via Safaricom M-Pesa.
Kilimo Salama
Kilimo Salama, Kiswahili for “safe farming”, is a crop insurance product offered by the Sygenta Foundation for Sustainable Agriculture. Kilimo Salama enables farmers to pay crop insurance premiums and receive payouts via Safaricom M-Pesa.